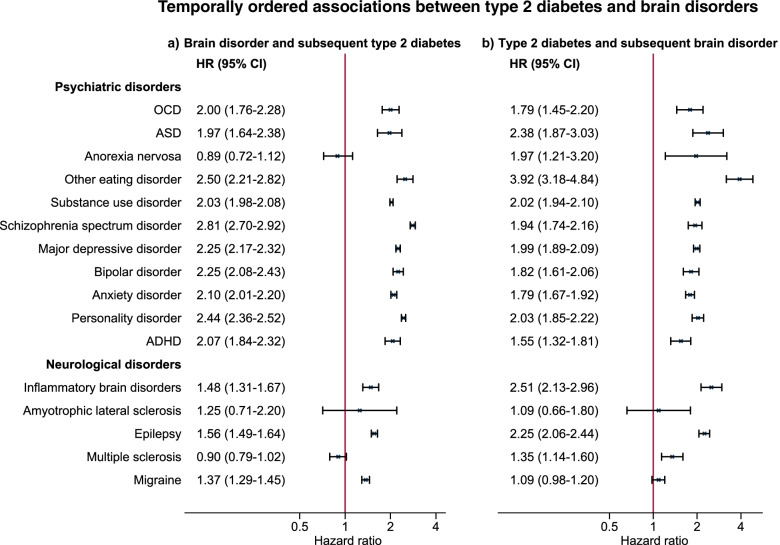
Fig. 2.
Adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) based on temporally ordered analyses for the association between type 2 diabetes and included psychiatric and neurological disorders. Analyses were adjusted for sex, birth year, and parental history of psychiatric disorders and type 2 diabetes. a Individuals (n = 1,883,198) were followed for type 2 diabetes from age 30 until end of follow-up, and the brain disorder of interest were included as a time-dependent exposure variable after age 30, and time-fixed for disorders diagnosed before age 30. N = 1,883,198 b Individuals were followed for the brain disorder of interest from age 30 until end of follow-up, and type 2 diabetes status was included as a time-dependent exposure. For the last approach (type 2 diabetes and subsequent brain disorder), only incident cases were included and hence the total number of individuals included in each analysis varied for each outcome, e.g. for OCD as the outcome (n = 1,880,480) and for ASD as the outcome (n = 1,881,576). Minimally adjusted estimates as well as number of exposed cases can be seen in Supplementary Table 2. Abbreviations: ADHD: attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, ASD: Autism spectrum disorder, OCD: Obsessive-compulsive disorder