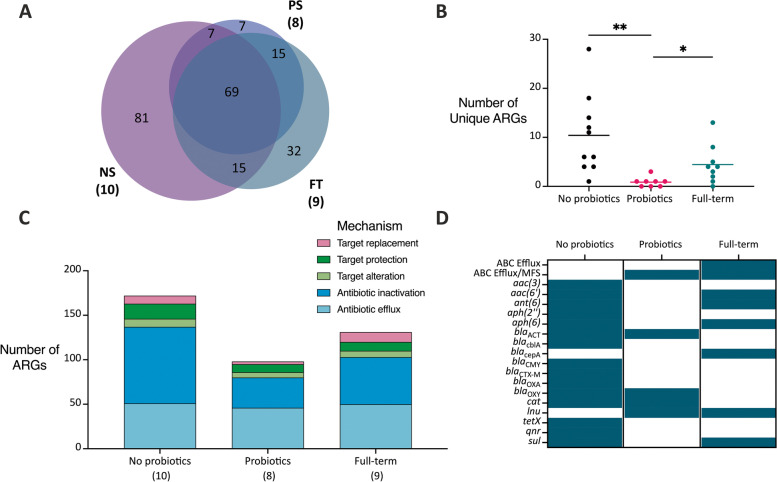
Fig. 2.
Differences in the resistome identified through RGI bwt in infants at visit 1. Reads were mapped to CARD using bowtie2, and antibiotic resistance genes with at least 100 reads were reported. The data presented is from the full set of preterm and full-term infants and at visit 1. A) Unique and overlapping ARGs identified in each infant group. The number of infant samples included in each is shown next to the sample type. B) The number of unique ARGs identified in each infant. Significant differences are denoted by a line and asterisk(s) above the groups that were compared (P = 0.0047 for NS vs PS, P = 0.0262 for PS vs FT). C) A breakdown of the mechanisms of antibiotic resistance identified in each infant group. The number of infant samples included in each is shown next to the sample type. D) The presence or absence of selected AMR gene families in each infant group. A teal box indicates that at least one gene from that AMR gene family was identified in any of the infant samples (NS = not supplemented preterm, PS = probiotic-supplemented preterm, and FT = full-term infants)