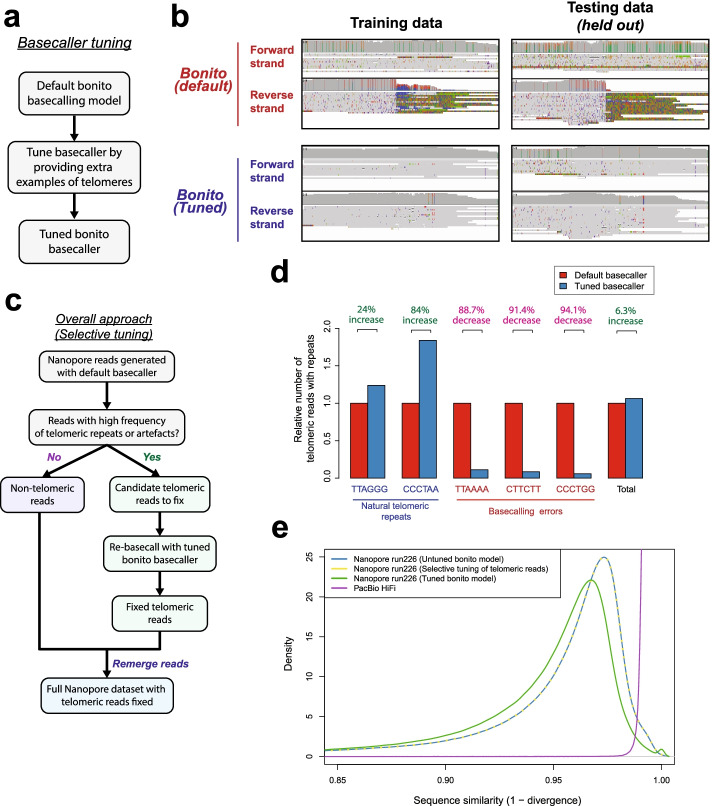
Fig. 2.
Selective re-basecalling of telomeric reads resolves basecalling errors at telomeres. a Approach for tuning the bonito basecalling model for improving basecalls at telomeres. b Tuned bonito basecalling model leads to improvement in basecalls at telomeric regions. IGV screenshots of the telomeric region (chr2q) in the CHM13 dataset basecalled using the default bonito basecaller, and the tuned bonito basecalling model is as depicted. c Overall approach for selecting and fixing telomeric reads in nanopore sequencing datasets. Telomeric reads are selected (“Methods”) and rebasecalled using the tuned bonito basecalling model. d The selective tuning approach leads to improved recovery of telomeric reads, and a decrease in the number of reads with basecalling artefacts. Evaluation was performed on the held-out test dataset (run226). e The “selective tuning” approach leads to little detected negative impact on basecalling of other genomic regions. The sequence similarity of all reads to the reference genome for three approaches for basecalling of nanopore reads was evaluated. They are applying the default bonito basecalling model to all reads (untuned bonito model), applying the tuned bonito basecalling model to all reads (tuned bonito model), and applying the tuned bonito basecalling model selectively to telomeric reads only (selective tuning of telomeric reads). The density plot depicts the sequence similarity of each read against the CHM13 reference genome as assessed using minimap2