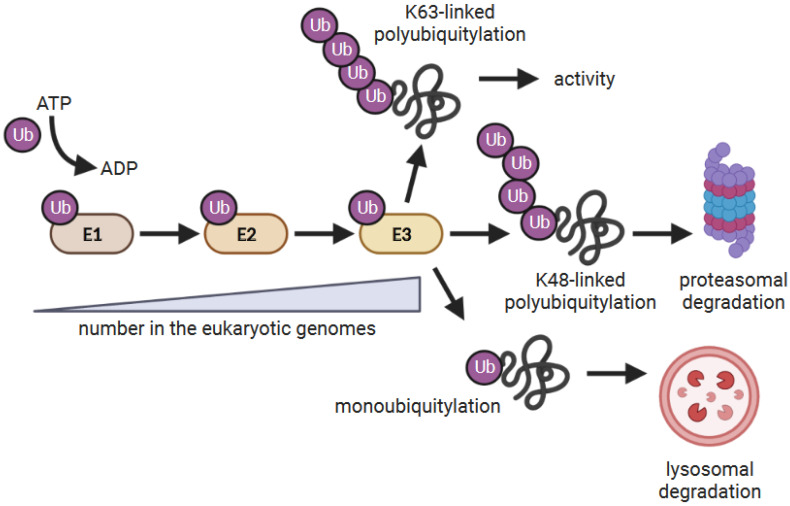
Figure 1.
The ubiquitylation reaction. E1 Ub-activating enzymes are charged with Ub and transfer the Ub to E2 Ub-conjugating enzymes. E2 enzymes either directly or indirectly associate with E3 Ub ligases which facilitates the ubiquitylation of substrates. Some E3s have E2 and substrate-binding domains as part of the same polypeptide, while others function as multiple protein complexes where E2 and substrate binding are mediated by different proteins. The consequence of ubiquitylation depends on how the target proteins are modified by Ub [26,27]. Proteins modified with a single Ub (monoubiquitylated) are often targeted to the lysosome for degradation, whereas proteins modified with lysine (K)-48-linked poly Ub chains are targeted to the proteasome for degradation. K63-linked poly Ub chains are often associated with altering protein function.