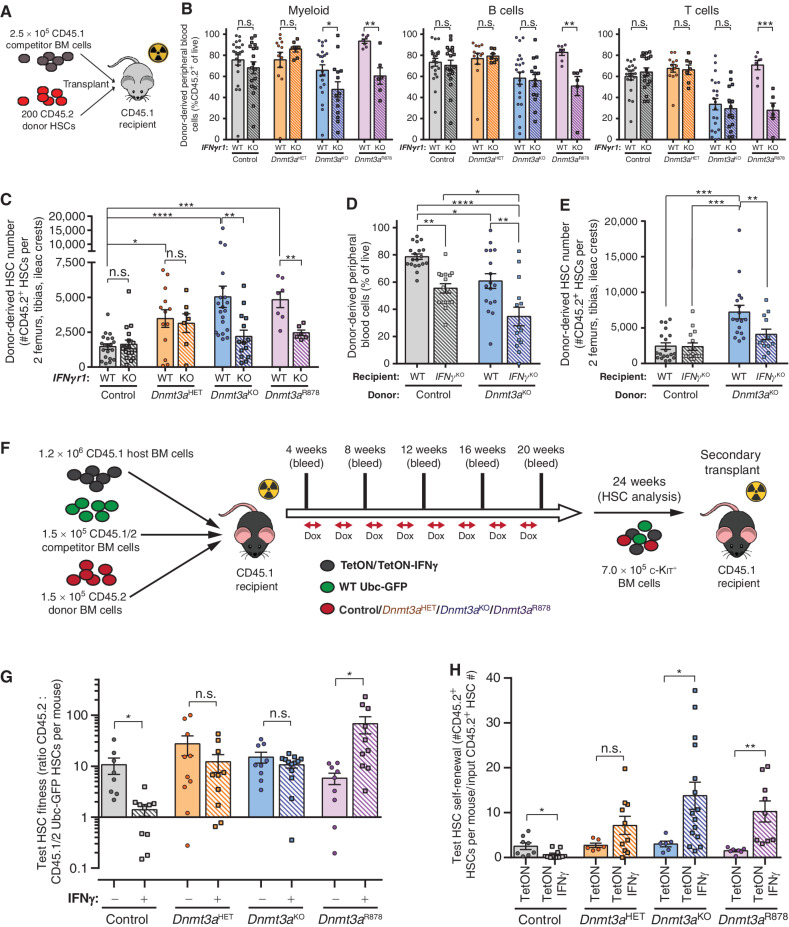
Figure 3.
IFNγ signaling is required for clonal expansion of Dnmt3a-mutant HSCs. A, Schematic of competitive HSC transplantation. B, Donor-derived chimerism in peripheral blood lineages 16 weeks posttransplant (n = 6–21). C, Number of donor-derived HSCs (CD45.2+Lineage−c-Kit+EPCR+CD48−CD150+) in BM of recipients 18 weeks posttransplant (n = 6–21). D, Donor-derived chimerism in peripheral blood 16 weeks posttransplant in wild-type (WT) or IFNγKO recipients (n = 14–19). E, Number of donor-derived HSCs in BM of recipients 18 weeks posttransplant (n = 14–19). F, Schematic showing CH competition model. G, Test HSC fitness ratio 24 weeks posttransplant in CH competition model (n = 8–13). H, Number of test HSCs (CD45.2+Lineage−c-Kit+EPCR+CD48−CD150+Ubc-GFP−) generated in BM of secondary recipients 18 weeks posttransplant per input HSC from primary transplant shown in G (n = 7–15). One-way ANOVA (D and E) or two-tailed t test (B, C, G, and H; data are compared for treatment/condition relative to parental genotype); *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. Data represent mean ± SEM.