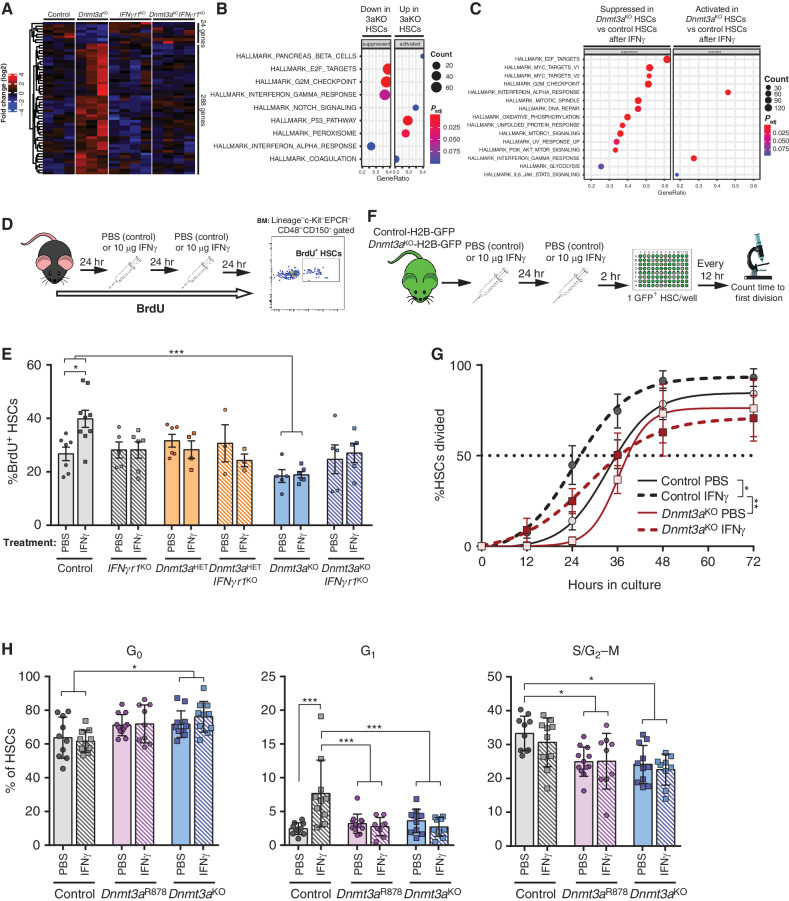
Figure 4.
Dnmt3a-mutant HSCs retain quiescence after IFNγ challenge. A, Expression pattern of differentially expressed genes (DEGs; P < 0.05, fold-change >2) between control and Dnmt3aKO HSCs across IFNgr1KO and Dnmt3aKOIFNgr1KO HSCs. B, Gene-set enrichment analysis (GSEA) comparison of control and Dnmt3aKO HSCs at baseline showing suppression of cell cycle–related genesets in Dnmt3aKO HSCs and activation of p53 targets. C, GSEA comparison of control and Dnmt3aKO HSC after acute IFNγ challenge. D, Schematic of BrdU incorporation assay to assess HSC proliferative responses. E, Percentage of BrdU+ HSCs (Lineage−c-Kit+EPCR+CD48−CD150+) from indicated genotypes after 72-hour timecourse and treatment with either PBS or IFNγ (n = 3–9). F, Experimental workflow for single HSC division assays using H2B-GFP-labeled HSCs. G, Time to first division of HSCs (GFP+Lineage−c-Kit+EPCR+CD48−CD150+) in response to PBS or IFNγ treatment (mean ± SEM plus line of best fit, n = 5–6). H, Flow cytometric Ki67/7AAD cell-cycle analysis of HSCs (Lineage−c-Kit+EPCR+CD48−CD150+) from PBS- or IFNγ-treated mice following 26-hour culture to stimulate proliferation (n = 9–12). One-way ANOVA (E and H) or two-way ANOVA (G); *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001. Data represent mean ± SEM.