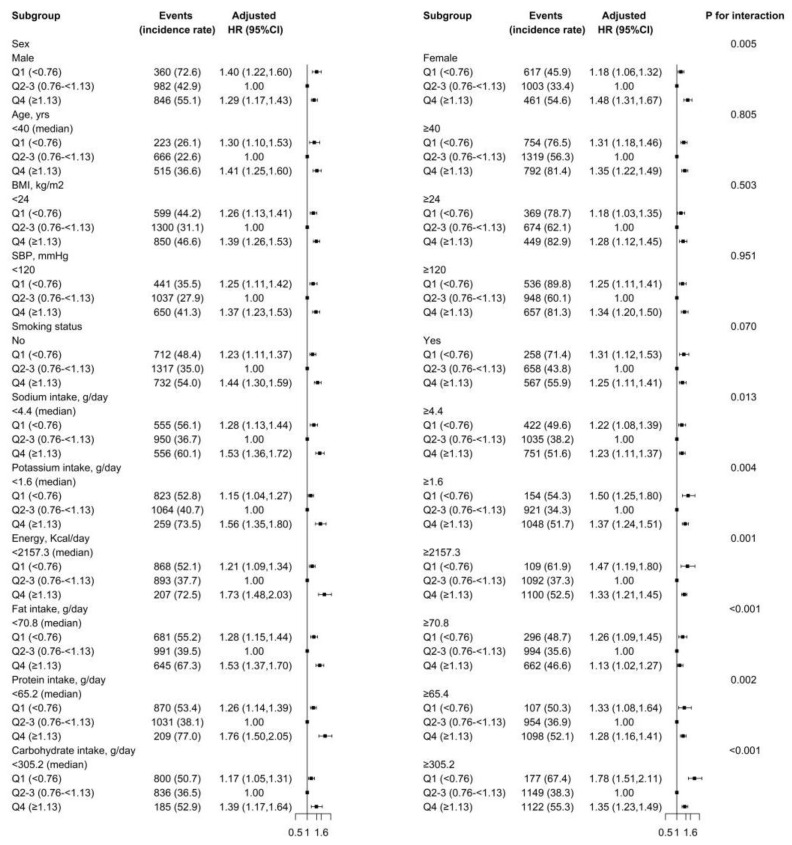
Figure 2.
The relation of dietary thiamine intake (Q1 vs. Q2–3 vs. Q4) with risk of new-onset hypertension in various subgroups. Adjusted for sex, age, body mass index, survey year, regions, SBP, DBP, alcohol drinking, smoking, urban or rural residents, education levels, occupations, physical activity, intakes of energy, sodium and potassium, if not stratified.