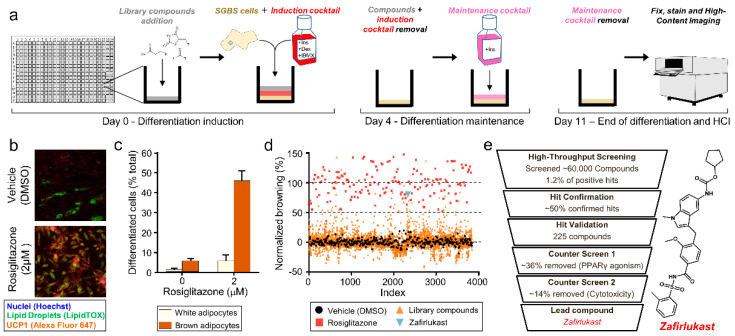
Figure 1.
High-throughput screening reveals an inducer of brown fat differentiation. (a) Schematic of SGBS cells differentiation procedure. Human SGBS preadipocytes in media containing insulin, dexamethasone, and IBMX were plated directly on the compound in a 384 well-plate for induction. The induction media was then removed after 4 days and replaced with maintenance media containing only insulin for an additional 7 days. After 11 days, the plates were fixed, permeabilized, and stained for imaging. (b) SGBS treated with rosiglitazone served as positive controls for each plate. Cells were co-stained with anti-UCP1 antibodies (red), LipidTox (green) for lipid droplets, and Hoechst (blue) to visualize nuclei. (c) Quantification of rosiglitazone-induced brown adipocytes. Adipocytic differentiation rate was calculated based on an algorithm that identifies the area and intensity of lipid droplets and UCP1 staining. Brown adipocytes met a set threshold that contains lipid droplets in addition to UCP1 protein. Differentiated cells that have lipid droplets but no UCP1 were defined as white adipocytes. (d) Scatter plot representing a randomly selected batch of screening data (4000 of the total ~60,000 compounds screened). Each data point represents a single compound at 5 μM, normalized to the DMSO control (black). Rosiglitazone (red) at 2 μM served as a control. Zafirlukast is highlighted in light blue. (e) Schematic of preadipocyte screening and high-throughput workflow. Compounds were selected through hit confirmation and validation and then prioritized based on (1) bias for brown adipocytes versus white adipocytes, (2) lack of direct PPAR-γ agonism, and (3) lack of cytotoxicity. Zafirlukast matched our criteria for inducers of brown fat and became the basis of further investigation.