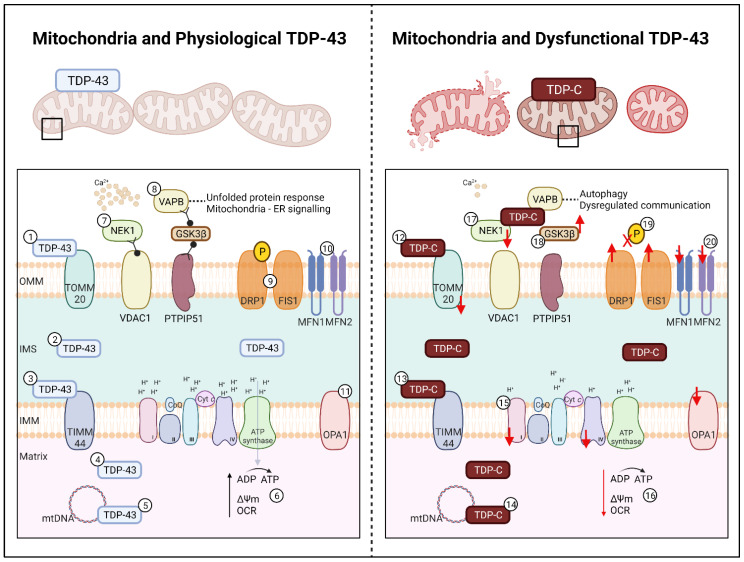
Figure 2.
Effect of TDP-43 on Mitochondria in ALS. Left: Mitochondria and Physiological TDP-43. In healthy cells length TDP-43 localises to (1) TOMM20 on the OMM, (2) within the IMS and to (3) TIMM44 of the IMM, (4) freely within the matrix, and (5) regulates mtDNA for OXPHOS complex expression. (6) OXPHOS complexes I-IV and ATP synthase facilitate ATP production, facilitating the maintenance of the membrane potential and a healthy oxygen consumption rate. (7) Mitochondrial proteins NEK1 and VDAC1 support calcium signalling. (8) The mitochondrial-endoplasmic reticulum complex, PTPIP51-GSK3β-VAPB ensures proper protein folding and organelle communication. The mitochondrial dynamics related proteins for (9) fission on the OMM (DRP1, FIS1) and (10) fusion on the OMM (MFN1, MFN2) and the (11) IMM (OPA1) facilitate mitochondrial network homeostasis and regulation. Right: Mitochondria and Dysfunctional TDP-43. In ALS, fragmented TDP of 25 kDa and 35 kDa (denoted as TDP-C) localises to (12) TOMM20 and (13) TIMM44 causing downregulation and loss of mitochondria. TDP-C also co-localise to (14) mtDNA causing fragmentation, leading to a (15) loss of OXPHOS complex I and IV. (16) Loss of complex regulation leads to a decrease in ATP production, driving a loss of membrane potential and oxygen consumption rate. (17) TDP-C leads to a decrease in NEK1, causing a loss of VDAC1 and calcium signalling. (18) Localisation of TDP-C to GSK3β causes the loss of mitochondrial-endoplasmic reticulum signalling resulting in protein folding dysfunction and loss of organelle communication, which in turn leads to autophagy. Further impacts of TDP-C results in (19) DRP1 de-phosphorylation leading to (20) increased fission and decreased fusion. Upregulation of FIS1 and downregulation of MFN1, MFN2, and OPA1 are also observed in TDP-43 models leading to increased fission and mitochondrial fragmentation and subsequent cellular death. TDP-C; TDP-43 C-terminal fragments, OMM; outer mitochondrial membrane, IMS; inter-membrane space, IMM; inner mitochondrial matrix, ATP; adenosine triphosphate, CoQ; Coenzyme Q; Cyt c; cytochrome c. Created with BioRender.com accessed on 12 July 2022.