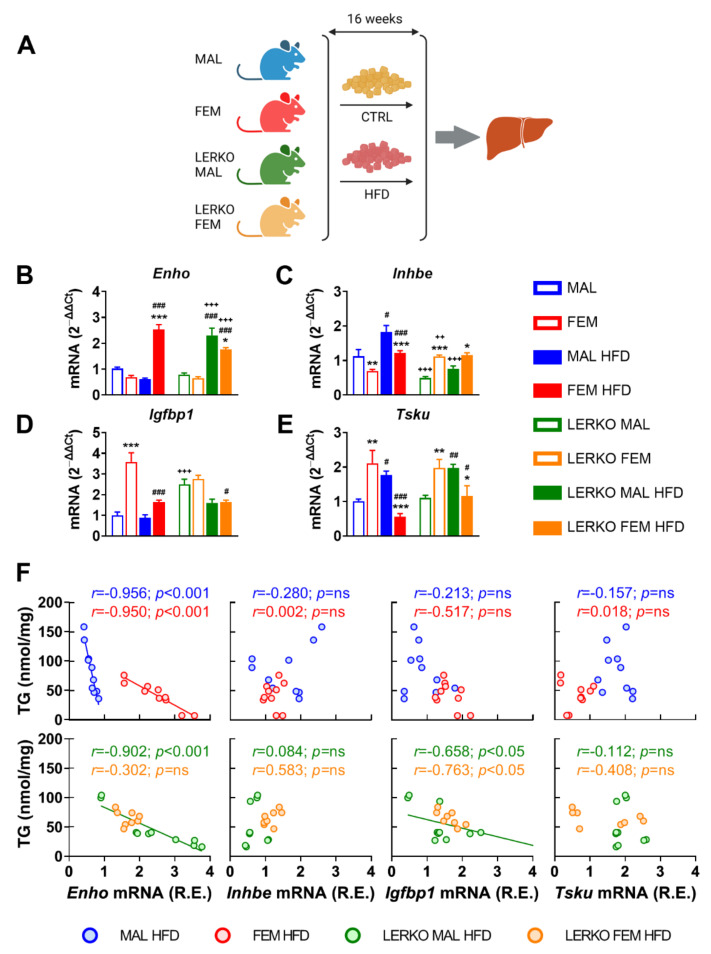
Figure 4.
Enho mRNA levels negatively correlate with fatty liver in a HFD-induced mouse model of NAFLD. (A) Experimental design adopted to evaluate the relevance of estrogen signaling in the liver metabolic response to a high-fat diet (HFD). (B–E) mRNA contents of Enho (B), Inhbe (C), Igfbp1 (D), and Tsku (E) measured by RT-PCR in the liver of male and female control and LERKO mice fed with control diet or HFD. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 8–10). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001 females vs. males; # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, and ### p < 0.001 HFD vs. control diet; ++ p < 0.01 and +++ p < 0.001 LERKO vs. control mice by two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test. (F) Pearson’s correlation and linear regression between liver triglyceride (TG) content and relative expression (R.E.) of Enho, Inhbe, Igfbp1, and Tsku mRNA levels measured in the liver of male and female control and LERKO mice fed with HFD.