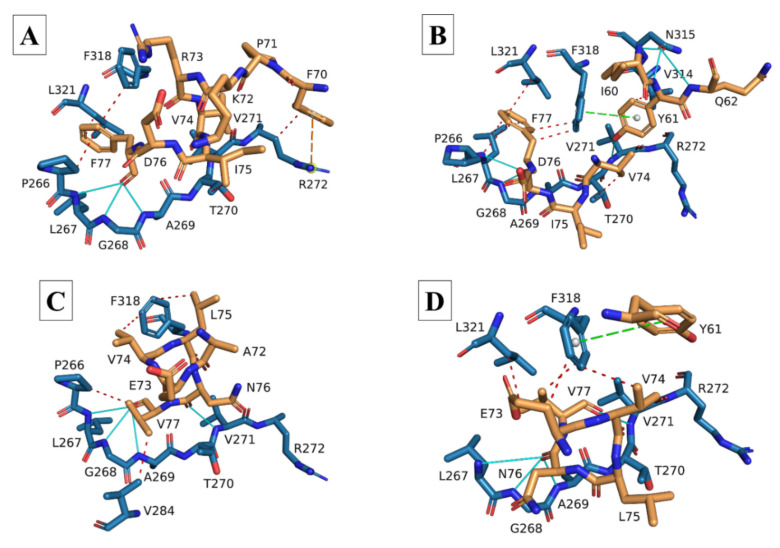
Figure 5.
Stick models of the modelled 8-mer and 18-mer envelope (E) peptides of the less virulent HCoV-229E and HCoV-NL63 E proteins docked to the PALS1 PDZ domain. (A) Stick model of the modelled HCoV-229E (8-mer) E peptide (gold) docked to the PDZ domain of the PALS1 protein (blue). (B) Stick model of the modelled HCoV-229E (18-mer) E peptide (gold) docked to the PDZ domain of the PALS1 protein (blue). (C) Stick model of the modelled HCoV-NL63 (8-mer) E peptide (gold) docked to the PDZ domain of the PALS1 protein (blue). (D) Stick model of the modelled HCoV-NL63 (18-mer) E peptide (gold) docked to the PDZ domain of the PALS1 protein (blue). Peptides in (A–D) were produced from the homology-modelled E proteins of the respective hCoVs and docked to the partial PALS1 protein (PDB ID: 7NTK) using the HADDOCK webserver. Docked E peptides with the lowest RMSD values compared to the 7NTK experimental E peptide were uploaded to the protein–ligand interaction profiler (PLiP) webserver to demonstrate the types of interactions between PALS1 and the E peptides. Red, dashed lines: hydrophobic interactions; Cyan, solid lines: hydrogen bonds; Yellow, dashed lines: ionic interactions (salt bridges); Green, dashed lines: cation-π interactions.