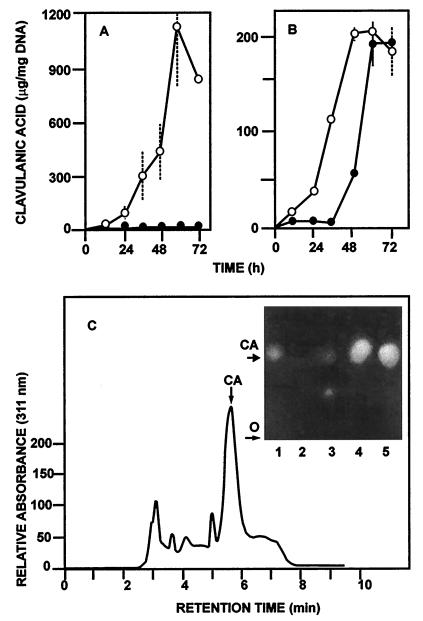
FIG. 4.
Production of clavulanic acid by wild-type S. clavuligerus 27064 (○) and replacement mutant S. clavuligerus pyc::aph-b (●) in SA (A) and GSPG (B) media. (C) HPLC elution profile of the broth corresponding to 48 h of S. clavuligerus pyc::aph-b growth in GSPG medium shown in panel B. The arrow indicates the peak that coeluted with a sample of pure clavulanic acid (CA). (Inset) Bioautography of a paper chromatography of culture broths. Lanes: 1, pure clavulanic acid (Rf 0.67); 2 and 3, S. clavuligerus pyc::aph-b grown in SA medium; 4, S. clavuligerus 27064 grown in GSPG medium; 5, S. clavuligerus pyc::aph-b grown in GSPG medium. SD are given as discontinuous bars for the wild-type strain and as solid bars for the S. clavuligerus pyc::aph-b mutant.