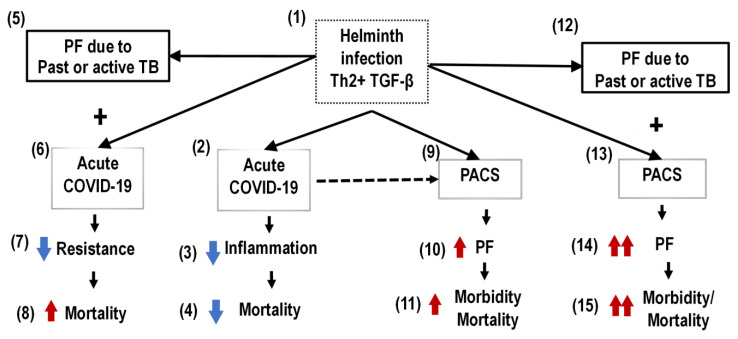
Figure 1.
Overlapping of acute COVID-19 and postacute COVID-19 syndrome (PACS) and tuberculosis (TB) in the helminth coinfection setting in sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) population. (1) Helminth coinfection inhibits inflammation and amplifies pulmonary fibrosis (PF) processes; (2–4) helminth coinfection inhibits COVID-19 lung inflammation and decreases mortality; (5–8) infection by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and PF due to past or active TB limit resistance to COVID-19 and increase mortality; (9–11) PACS, amplified by helminth infection, increases morbidity and mortality; (12–15) the overlapping of PF due to past or active TB with PF due to PACS, amplified by helminth infection, increases morbidity and mortality.