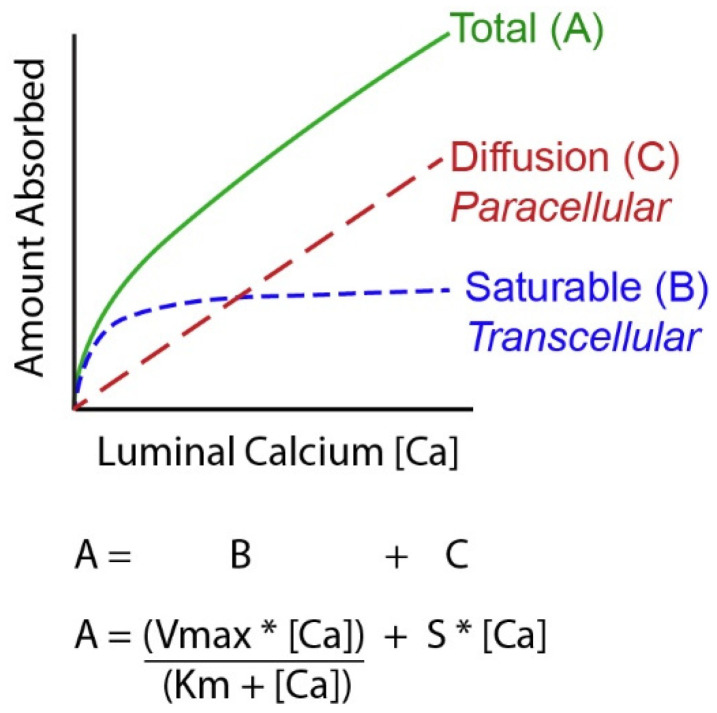
Figure 1.
A Mathematical model of intestinal calcium (Ca) absorption. By studying Ca absorption over a range of luminal Ca levels it has been shown that the total amount of Ca absorbed across the intestinal barrier can be described as a curvilinear function. Total transport (A) is the sum of a saturable component (likely transcellular, B) that can be defined by the Michaelis–Menten equation and a diffusional process (C) that is defined by a straight line. [Ca] = luminal Ca concentration; S = the slope of the diffusional component; Vmax = the maximum transport rate seen for the saturable transport component; Km = the luminal concentration of the mineral at ½ the Vmax.