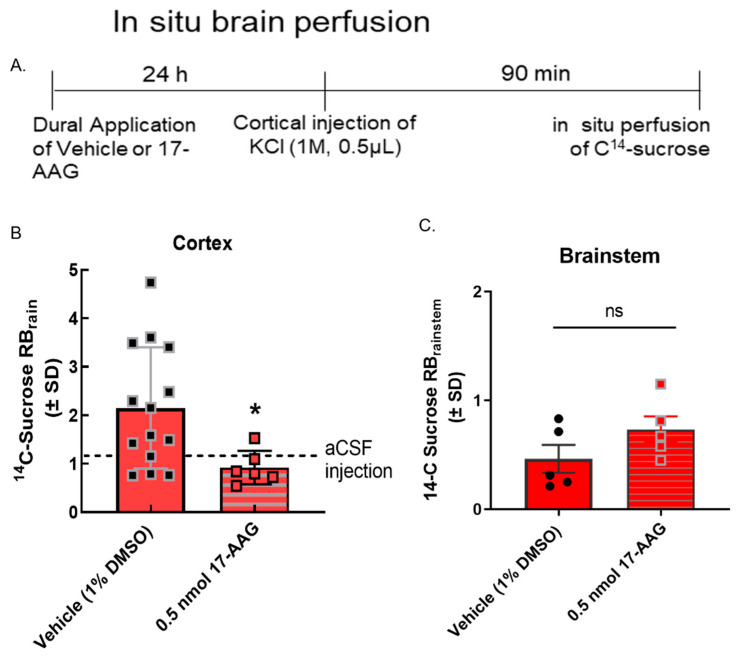
Figure 4.
17-AAG reduced cortical spreading depression-associated blood–brain barrier leak in vivo. Dural cannulation was performed on female Sprague Dawley rats. After recovery, they were injected with 17-AAG (0.5 nmol) or vehicle (1% DMSO in saline) via dural cannula 24 h before CSD induction. CSD was induced by injection of KCl (1 M) through dural cannula. In situ brain perfusion was performed 90 min after the cortical injection of KCl. (A) Timeline of treatment, cortical injection, and perfusion. (B) 14C-sucrose uptake was measured in whole cortex and presented as the brain to plasma ratio (RBr) after 10 min brain perfusion. Dural application of 17-AAG (0.5 nmol) 24 h before cortical injections significantly reduced 14C-sucrose uptake in cortex as compared to vehicle control, suggesting that HSP90 inhibition could prevent KCl-caused BBB leak. (KCl + 17-AAG vs. KCl + vehicle: * p < 0.05, assessed unpaired t-test.) Dotted line represents the 14C-surose uptake measured in aCSF-treated animals. (C) No statistically significant difference was observed in sucrose uptake in the brainstem (p = 0.17). Values are mean ± SEM (n = 6–11). Circles and squares indicate individual subjects.