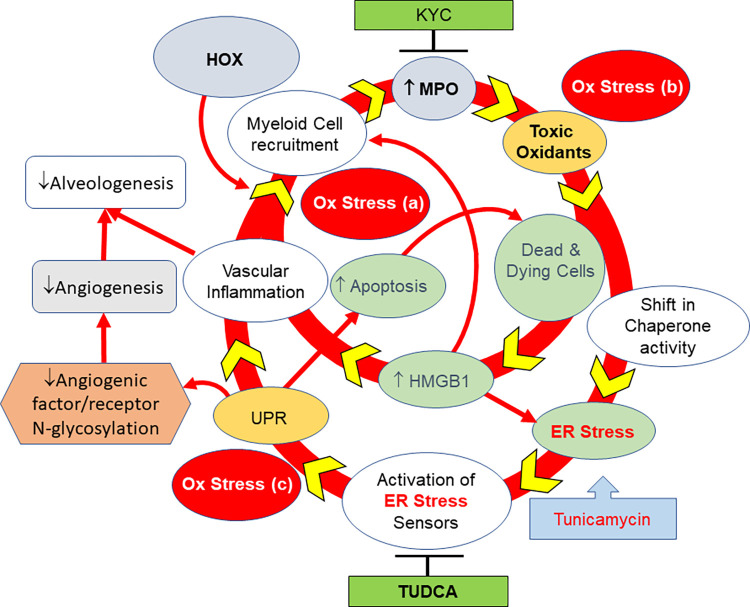
Fig 11. ER stress plays a critical role in propagating the cycle of destruction to cause BPD.
Supplemental oxygen initiates the cycle of destruction by generating oxidative stress and recruiting inflammatory cells. MPO released by the infiltrated myeloid cell generates toxic oxidants that produce ER stress. ER stress propagates the destruction cycle by causing more oxidative stress and inflammation. ER stress impairs angiogenesis by decreasing the N-glycosylation of angiogenic factors and their corresponding receptors, such as VEGFR2. Tunicamycin inhibits alveolar formation by inducing ER stress. TUDCA, a chemical chaperone, attenuates alveolar simplification by reducing ER stress elicited by either supplemental oxygen or tunicamycin. Our findings strongly indicate a mechanistic role of ER stress in BPD. The protective effect of KYC is believed to be mediated by its activity in repurposing MPO into a quasi-catalase that decreases the generation of toxic oxidants by MPO.