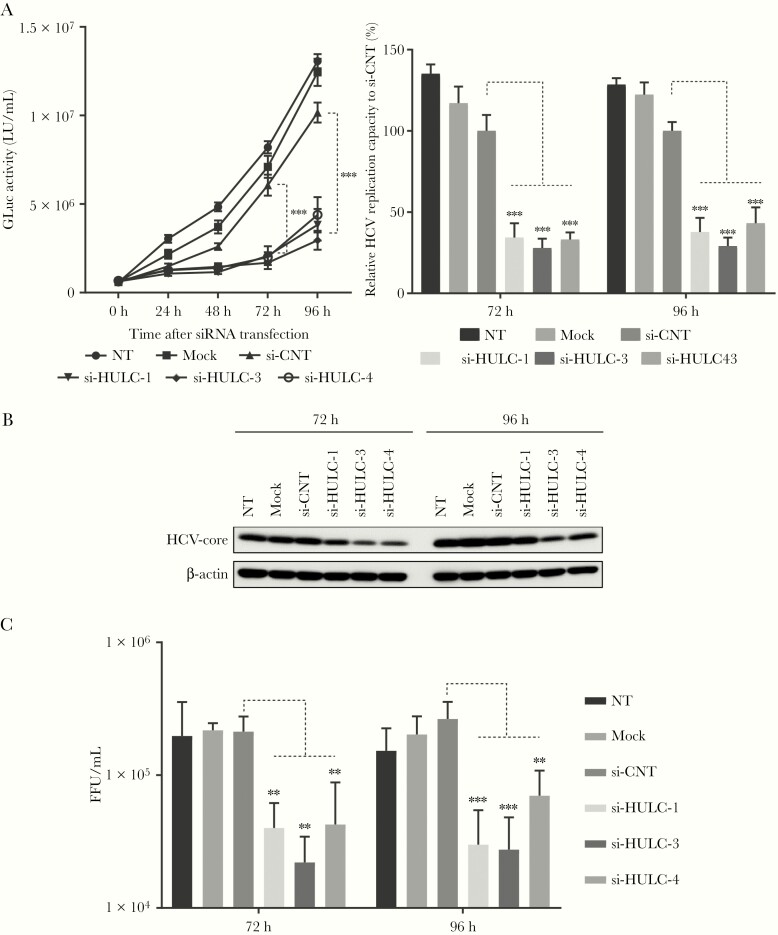
Figure 4.
Inhibition of hepatitis C virus (HCV) replication by HULC suppression. A, FT3-7 cells were transfected with HJ3-5/GLuc2A RNA or HJ3-5 RNA and 72 hours later, the cells were transfected with 3 different small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) targeting HULC (si-HULC-1, si-HULC-3, and si-HULC-3) and control siRNA (si-CNT) at 20 nM. The medium was replaced at 24-hour intervals, and secreted GLuc activity was determined until 96 hours. The left panel shows the time course of GLuc activity after siRNA transfection and the right panel shows relative GLuc activity 72 and 96 hours after siRNA transfection to that from si-CNT–transfected cells, which was set to 100. The differences of means were analyzed by 2-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). B, HCV core protein and β-actin expression in HJ3-5 RNA-transfected cells was analyzed by Western blot analysis with appropriate antibodies 72 and 96 hours after siRNA transfection. C, Medium from HJ3-5 RNA-transfected cells was replaced at 24-hour intervals until 96 hours, and the media collected at 72 and 96 hours were used to infect Huh-7.5 cells to determine infectious virus yield using a conventional focus-forming unit (FFU) assay. Differences in the means at each time point were analyzed by one-way ANOVA. **P < .01, ***P < .001. NT indicates nontreatment.