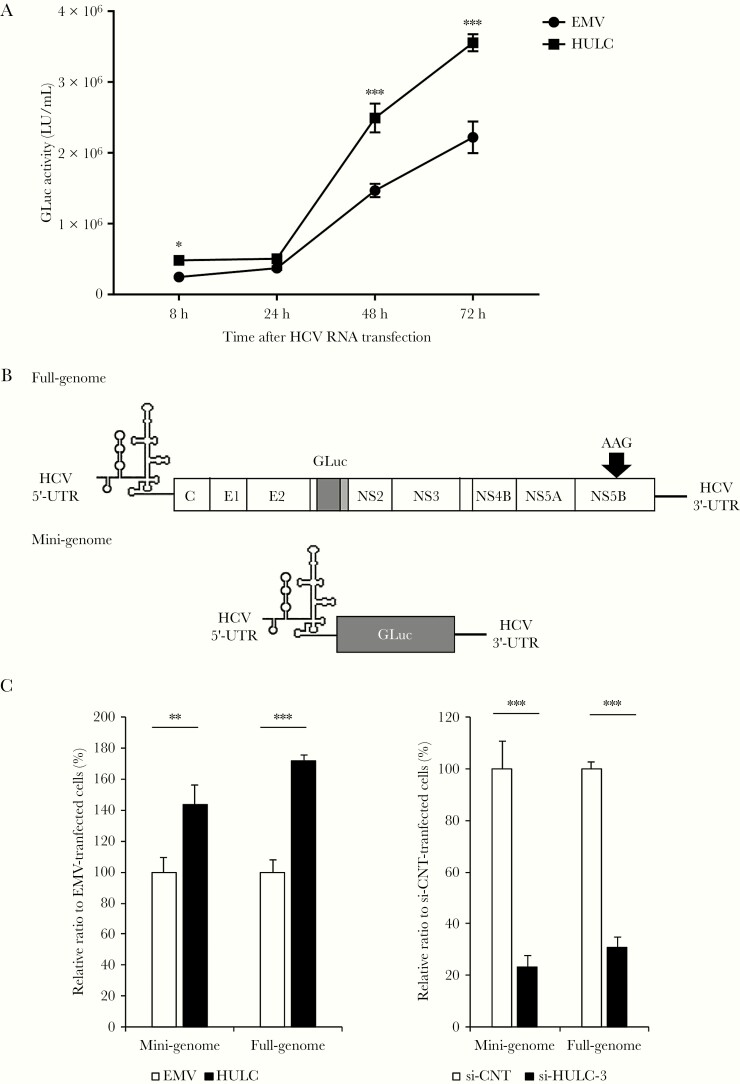
Figure 5.
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) replication is enhanced through HCV internal ribosome entry site (IRES)–directed translation. A, Huh-7.5 cells were transfected with a plasmid encoding HULC or an empty vector (EMV), and 24 hours later, they were transfected with HJ3-5/GLuc2A RNA. The medium was replaced at 24-hour intervals until 96 hours, and secreted GLuc activity was determined. Differences in the means of GLuc activity between EMV and HULC at each time point were analyzed with Student t test. B, Schematic representation of the nonreplicating RNAs used for the experiments for the effect of HULC on HCV IRES-directed translation. UTR indicates the untranslated region. C, Huh-7.5 cells were transfected with a plasmid encoding HULC or EMV, and 48 hours after transfection, the cells were transfected with full-genomic or mini-genomic RNA. Eight hours later, secreted GLuc activity was determined (left panel). Huh-7.5 cells were transfected with small interfering RNA (siRNA) targeting HULC or control siRNA (si-CNT) at 20 nM, and 48 hours after transfection, they were transfected with full-genomic or mini-genomic RNA. Eight hours later, secreted GLuc activity was determined (right panel). Differences in the means of relative ratios between CNT and HULC or si-CNT and si-HULC-3 were analyzed with Student t test. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001.