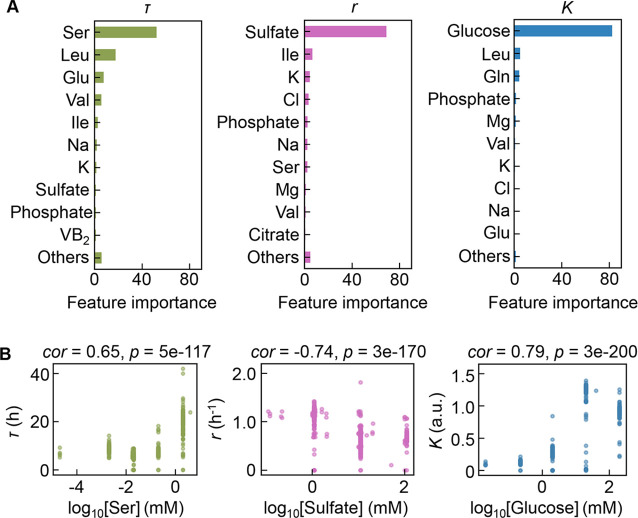
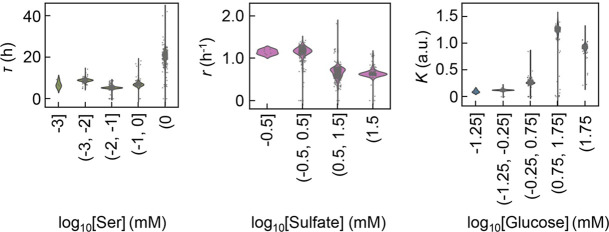
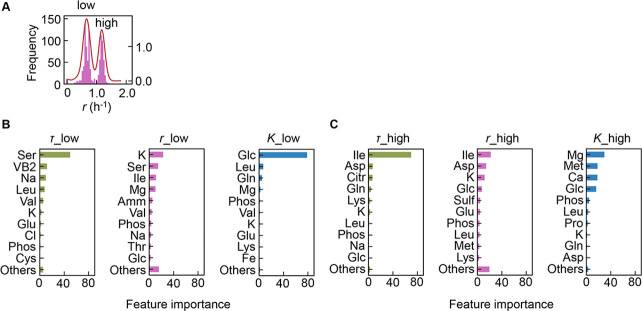
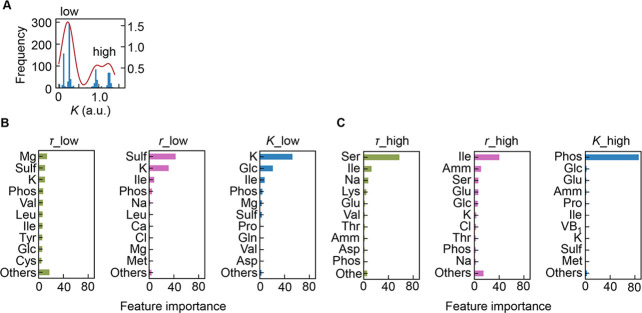
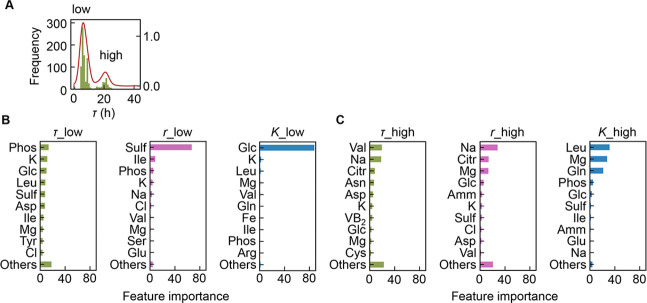
Figure 4. Contribution of the components to bacterial growth.
(A) Relative contributions of the components to the three parameters predicted by gradient-boosted decision tree (GBDT). 10 components with large contributions to the three parameters of lag time (τ), growth rate (r), and saturated population size (K) are shown in order. The remaining 31 components are summed as ‘Others’. (B) Correlation of the concentrations of the components with the growth parameters. The components with the largest contributions to the three parameters τ, r, and K are shown individually. Spearman’s correlation coefficients and the p values are indicated.