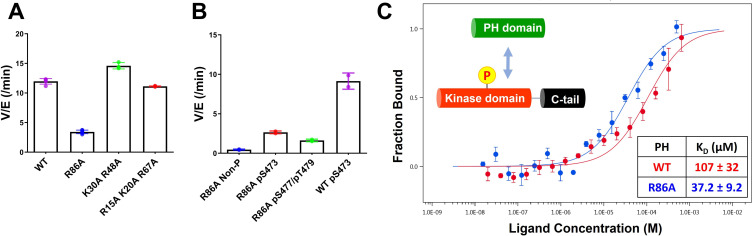
Figure 2. Kinase activities of Akt PH domain basic residue mutations and analysis of R86A PH domain intermolecular binding to the Akt kinase domain.
(A) Enzymatic activities of full-length Akt mutants possessing pT308 and pS477/pT479 (A1–A4) prepared using a three-piece expressed protein ligation (EPL) strategy. (B) Enzymatic activities of full-length R86A Akt mutant forms with differentially phosphorylated C-tails (A5: pS477/pT479, A7: Non-P, A11: pS473) relative to WT Akt containing pS473 (A10) as a control. These Akt forms were prepared using a two-piece EPL strategy. These kinase assays were performed in buffer containing 250 μM ATP and 20 μM GSK3 peptide as substrates (n≥3, SD shown). (C) MST (microscale thermophoresis) binding experiments using the N-terminally Cy5-labeled kinase domain with pT308 as a target protein and the isolated PH domain (WT or R86A) as a ligand. WT: red, R86A: blue (n=3, SEM shown).