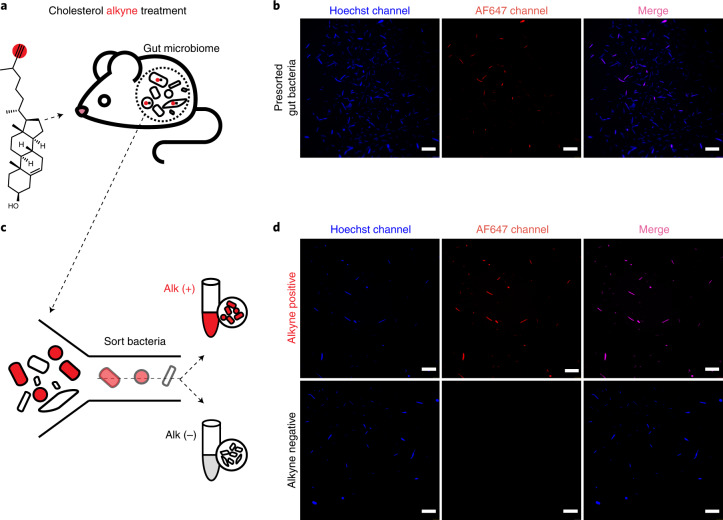
Fig. 1. Isolation of diet-derived cholesterol-interacting microbes using bio-orthogonal labelling and FACS.
a, Schematic showing treatment of mice with CholAlk to identify microbes that take up dietary cholesterol and derivatives of dietary cholesterol. b, Confocal microscopy detecting CholAlk-interacting bacteria from mouse caecal contents (n = 6, representative images from one mouse are shown). c, Schematic depicting FACS-based separation of microbial communities into cholesterol-interacting (Alk+) or not interacting (Alk−) populations. d, Confocal microscopy detecting the presence (alkyne positive, Alk+) or absence (alkyne negative, Alk−) of CholAlk derivatives in microbiome samples separated using FACS (n = 4, representative images from one mouse are shown). For confocal microscopy staining: blue, Hoechst 33342; red, Alexa Fluor 647-azide (AF647). Scale bar, 20 μm.