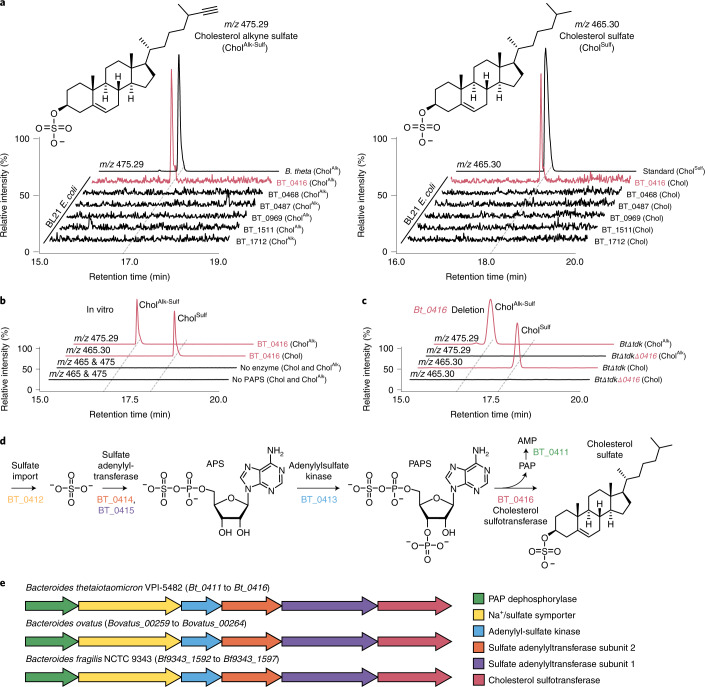
Fig. 4. A gene cluster in Bacteroides converts cholesterol to CholSulf.
a, Heterologous expression of cholesterol sulfotransferase candidates in BL21 E. coli treated with either CholAlk or cholesterol and ion chromatograms representing the detection of CholAlk-Sulf or CholSulf, respectively (n = 2 biological replicates per gene candidate, representative traces are shown here) b, In vitro conversion of cholesterol to CholSulf and CholAlk to CholAlk-Sulf via enriched His6_BT_0416 (n = 2 biological replicates per condition, representative traces are shown here) c, Ion chromatograms demonstrating that the Bt_0416 deletion mutant does not make CholSulf. d, Putative biosynthesis of PAPS followed by the biosynthesis of CholSulf in Bacteroides. Gene products are coloured according to the key in e. e, Biosynthetic clusters representing putative CholSulf biosynthesis genes in B. thetaiotaomicron, B. ovatus and B. fragilis. Chromatograms are scaled to the largest peak in each dataset. The red text highlights metabolic functions attributed to BT_0416.