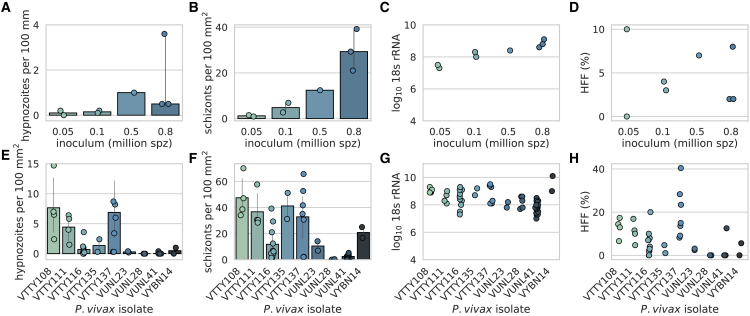
Figure 1.
Plasmodium vivax field isolates demonstrate robust primary infection in liver-chimeric humanized mice
Number of (A) hypnozoites (Spearman correlation r = 0.8) and (B) schizonts (Spearman correlation r = 0.964) observed per 100 mm2 of liver tissue section visualized 8 days post-infection using immunofluorescence assay (IFA). (C) Log10Plasmodium 18S rRNA copies per μg of liver quantified after liver harvest and RNA extraction (Pearson correlation r = 0.872). (D) Hypnozoite formation frequency (HFF) (%) observed per inocula (p = 0.506, Kruskal-Wallis test). Number of (E) hypnozoites and (F) schizonts present during the acute infection (5–8 days post-infection) for nine distinct P. vivax field isolates. (G) Log10Plasmodium 18S rRNA copies per μg of liver and (H) HFF for the same infections in (E–G). Each data point represents one animal. For microscopy counts, >3 liver tissue sections were counted per animal. The same parasite isolate (VTTY116) was used for (A–D). The number of sporozoites used for each infection in (E–H) was: VTTY108, VUNL23, VUNL28, VUNL41: 1,000,000; VTTY111: 600,000; VTTY116: 800,000; VTTY135; VTTY137: 500,000, and VYBN14: 850,000. Error bars represent 95% confidence interval.