Figure 1.
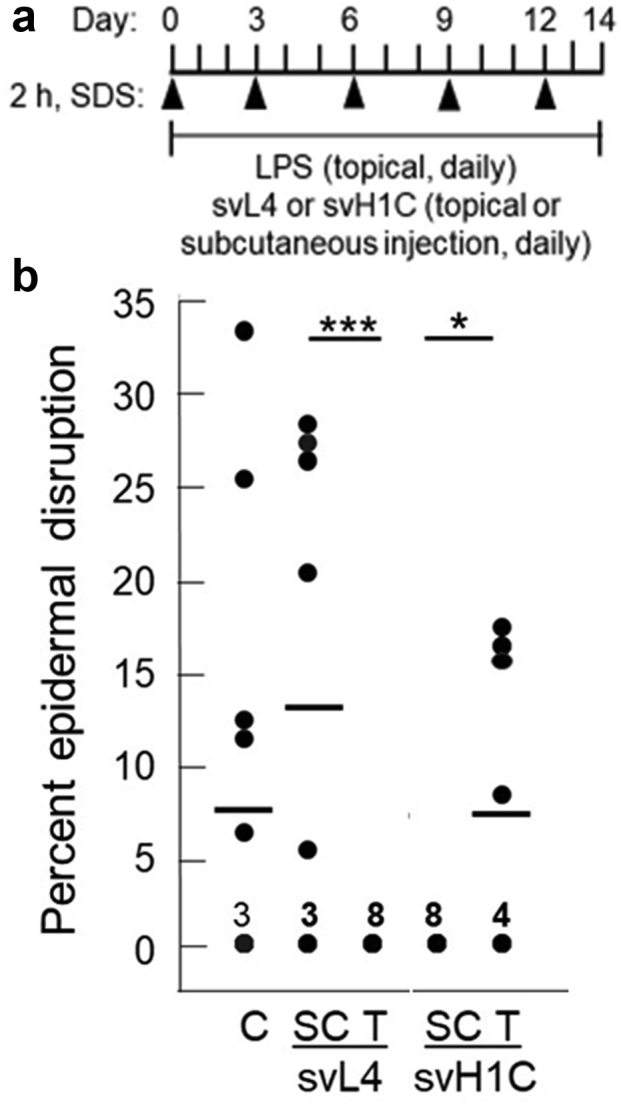
Extent of epidermal disruption after treatments with svL4 or svH1C. (a) Schematic of the experimental design after depilation of the skin. A 2-h treatment with 1% SDS was applied every 3 days. Eczema was induced by daily application of 200 μl of PBS containing 1 μg LPS per 1 cm2 area of the skin. svL4 or svH1C was added to the LPS solution to a final concentration of 1 μM for topical treatment (T). The peptides were injected subcutaneously at a dose of 1 nmol/g body weight (SC). (b) Two sections, one stained with H&E and the other with anti-Ly6G, were analyzed from each of the four mice in each group after 14 days of treatment (n = 8 for each group). The cumulative area of disruption of the epidermis is expressed as a percentage of the total length of 1-cm long sections. Dots indicate the values for each section, which ranged from zero to 33%. The number of sections that did not contain a disruption of the surface barrier and received a score of 0 is indicated for each group. Horizontal bars indicate mean values for each group. C depicts LPS-treated skin, which served as the control. Statistical data were analyzed, with all values per group, by one-way ANOVA test for pairs of treatment groups indicated by the bars at the top of the figure. ∗P = 0.022 and ∗∗∗P = 0.0056. C, control; h, hour; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; SC, subcutaneous; T, topical.
