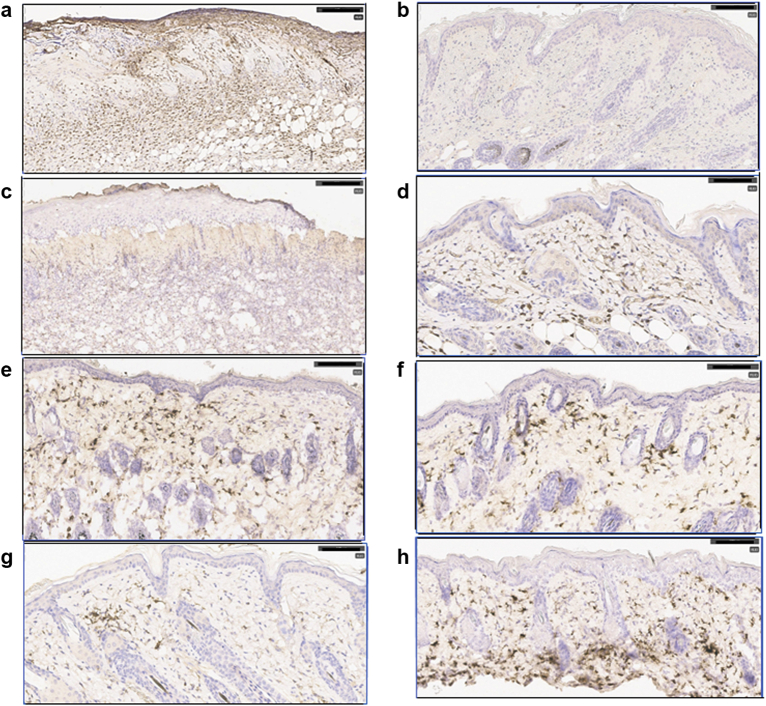
Figure 4.
Induction of eczema with SEB and HDM. Shown in the Figure are sections of skin treated for 5 days with svL4 or svL4 plus dexamethasone after a 4-day induction of eczema with SEB and HDM. Sections from all mice in the experiment shown in Figure 3 were viewed to select representative images for this figure. (a) Section stained with anti-Ly6G from a mouse treated with PBS after induction of eczema revealed extensive epidermal damage and a dense population of neutrophils. (b) svL4-treated skin had a restored epidermis and a dermis essentially free of neutrophils. (c) Section from the same mouse as in a stained with ER-MP23 (anti-CD301a/b), which revealed the absence of macrophages in areas that lacked a definition of the epidermal/dermal boundary. (d) Section from the same mouse as in b treated with svL4, which had a thin epidermis and an abundance of ER-MP23-stained macrophages. (e, f) svL4-treated skin stained with anti-CD301b. (g) Section of skin from a mouse treated with dexamethasone and stained with anti-CD11c, which contained a cluster of dendritic cells. (h) Section from a mouse treated with dexamethasone and stained with anti-CD301b. Positive staining is indicated by the brown color. The images are representative of mice in each group (n = 5). Bar = 100 μm. HDM, house dust mite; SEB, Staphylococcal enterotoxin B.