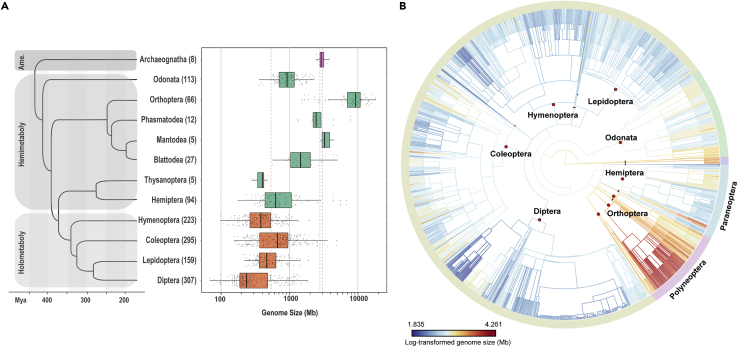
Figure 1.
Patterns of insect GS variation and evolution
(A) GS distribution pattern of 1,326 insect records from 12 orders along the time-calibrated phylogeny cited from Misof et al. (2014). Numbers of GS records in each order are shown in the brackets and orders with <5 species records are not demonstrated here. Dashed lines, of which colors represent the three types of insect metamorphosis (the ametaboly, insects without metamorphosis; the hemimetaboly, insects with incomplete metamorphosis; the holometaboly, insects with complete metamorphosis), indicate the averaged GS of corresponding metamorphosis groups. See also Tables 1, S1 and S2.
(B) Estimated evolution of 1,256 insects GS mapped onto the dendrogram according to the NCBI Taxonomy Tree, with all species names omitted. Colored branches reflect genome size values from small (dark blue) to big (dark red), generated based on the Brownian Motion (BM) process using the function of contMap in R package phytools (Revell 2012). Different insect orders are differentiated by red circles on the branches. The pinkish-purple outermost circle represents the cohort Polyneoptera and the light blue is for the cohort Paraneoptera. See also Table S1 and Figure S1.