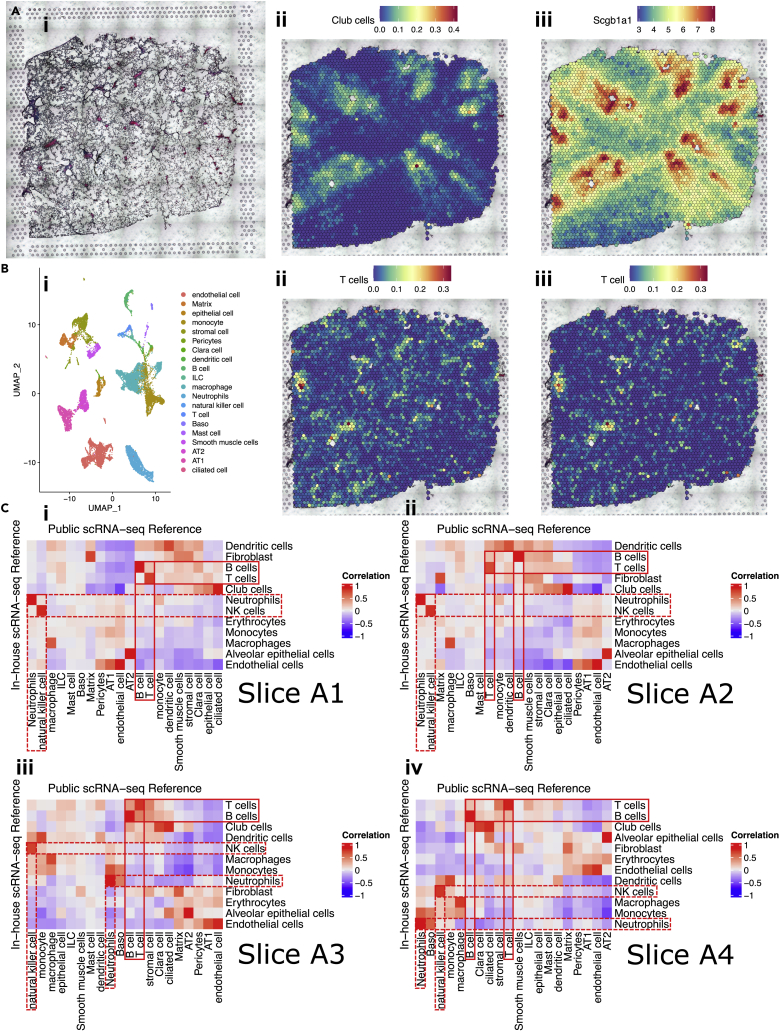
Figure 2.
Validation of the robustness of deconvolution method for spatial transcriptomics, see also Figure S2
(A) Proportion of club cells colocalizing with the expression of Scgb1a1 and the histological airways. (1) Histology of slice A3 showing the location of the airways. (2) Proportion of club cells across slice A3, deconvoluted using in-house scRNA-seq data. (3) Expression of Scgb1a1, a canonical marker for club cells, across slice A3.
(B) Proportions of T cells deconvoluted using the two independent scRNA-seq references were quite similar. (1) UMAP plot of 20 lung cell types identified in Cohen et al.’s public scRNA-seq data (GEO: GSE119228). (2) Proportion of T cells across slice A3, deconvoluted using in-house scRNA-seq data. (3) Proportion of T cells across slice A3, deconvoluted using Cohen et al.’s public scRNA-seq data.
(C) (i–iv) Correlation heatmap visualizing the proportions of cell types deconvoluted using in-house (in rows, 12 types) and public (in columns, 20 types) scRNA-seq data were highly correlated in slice A1-A4. Pearson’s r values were indicated by the color bars. Red boxes with solid lines highlighted selected adaptive immune cells, T cells and B cells. Red boxes with dashed lines highlighted selected innate immune cells, neutrophils and NK cells.