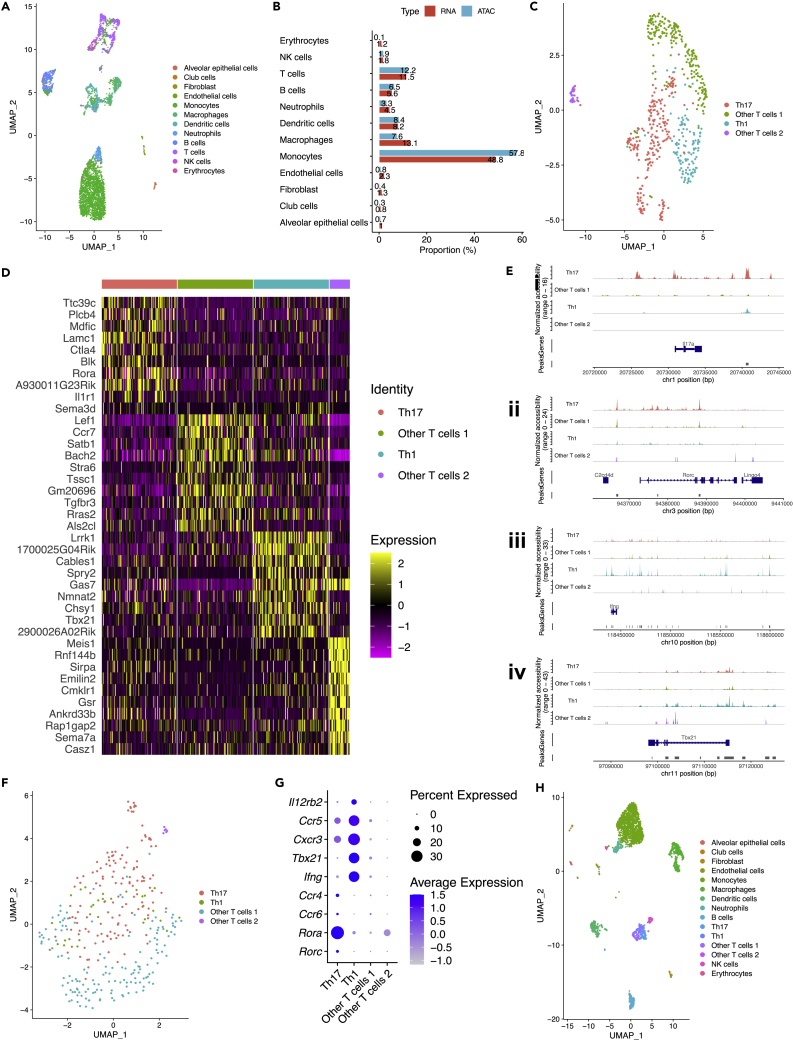
Figure 3.
Identification of subtypes of T cells by integrating scRNA-seq and scATAC-seq data, see also Figure S3
(A) UMAP plot of 12 lung cell types in scATAC-seq data identified via label transfer.
(B) Bar plot showing proportions of 12 cell types in scRNA-seq and scATAC-seq data were quite similar.
(C) UMAP plot of four subtypes of T cells in scATAC-seq data.
(D) Heatmap showing top 10 (by log2-Fold Change) markers (gene activity scores calculated using peaks) for each subtype of T cells in scATAC-seq data.
(E) (i–iv) Peaks in genomic regions around Il17a, Rorc, Ifng, and Tbx21, canonical markers for Th17 and Th1 cells.
(F) UMAP plot of four subtypes of T cells in scRNA-seq data identified via label transfer.
(G) Dot plot showing selected canonical markers for Th17 and Th1 cells in scRNA-seq data.
(H) UMAP plot of 15 lung cell types (including four subtypes of T cells) in scRNA-seq data.