A list of FDA and EMA approved chemotherapeutic nucleosidic analogs.
| Name | Structure | Statusa | Chemical modification | Targeted cancer | Mechanism of action | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fluorouracil |
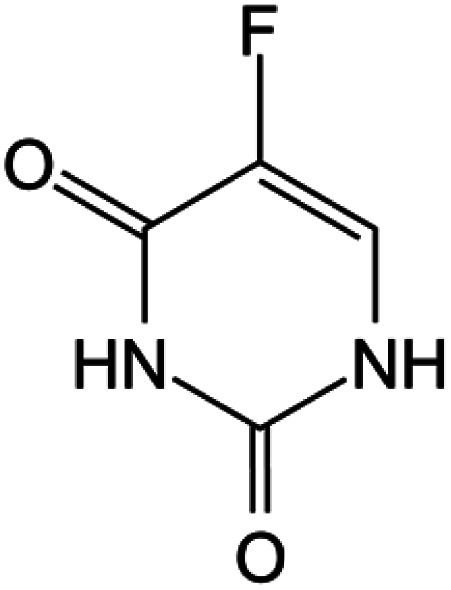
|
FDA approved (1962) | • Uracil modification by F-halogenation | • Colon, esophageal, stomach, pancreatic, breast, and cervical cancers | • Enzymatic inhibition | 37 |
| EMA approved (NA) | ||||||
| Floxuridine |
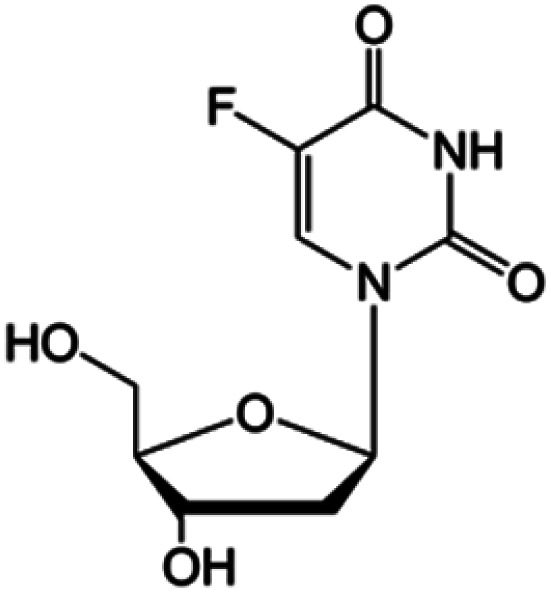
|
FDA approved (1970) | • Cytosine modification by F-halogenation | • Colon cancer | • Enzymatic inhibition | 38 |
| • DNA synthesis inhibition | ||||||
| Cytarabine |
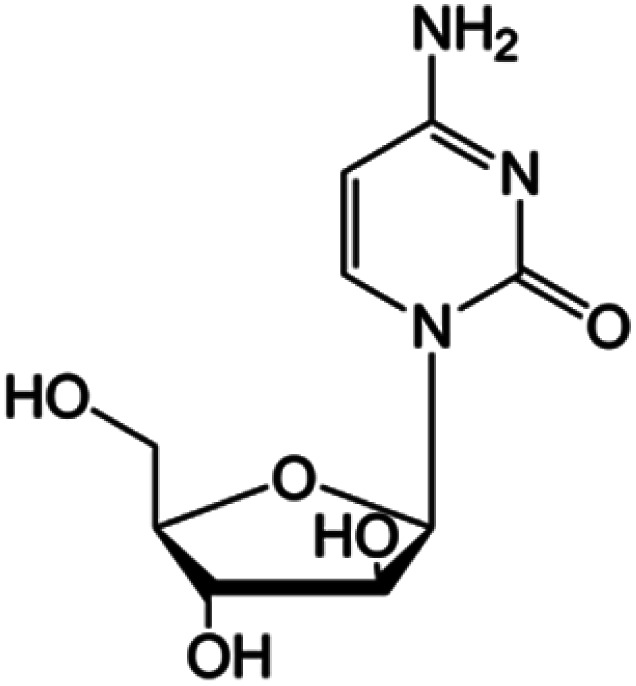
|
FDA approved (1969) | • Replacement of the ribose sugar ring with an arabinose | • Acute myelogenous leukemia | • DNA polymerase inhibition | 5 |
| EMA approved (2001) | • Lymphoblastic leukemia | |||||
| Gemcitabine |
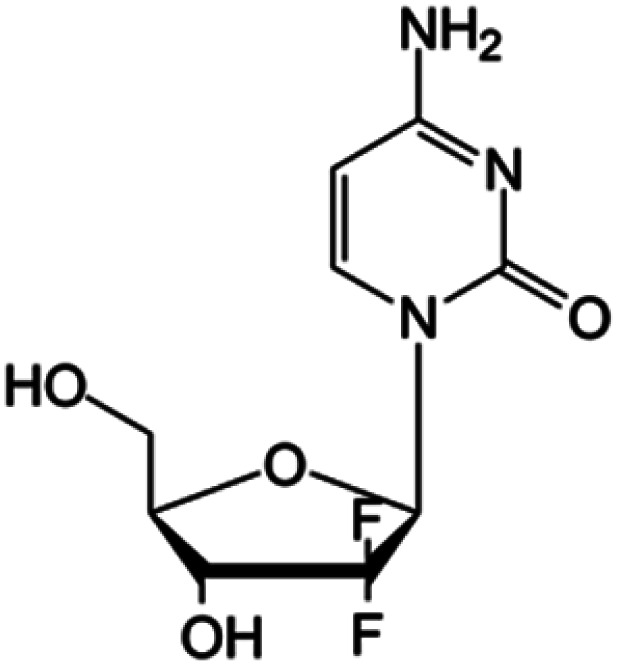
|
FDA approved (1996) | • Sugar ring F-halogenation | • Pancreatic, lung, breast, and bladder cancers | • Enzymatic inhibition | 7 |
| EMA approved (2008) | ||||||
| Azacitidine |
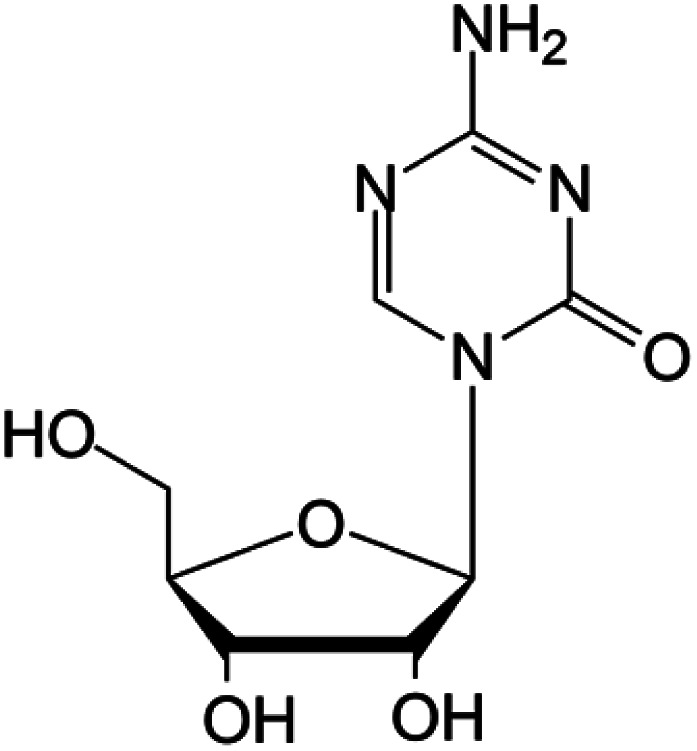
|
FDA approved (2004) | • Cytosine modification by azotation | • Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) | • DNA hypomethylation | 39 |
| EMA approved (2008) | • Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) | |||||
| Decitabine |
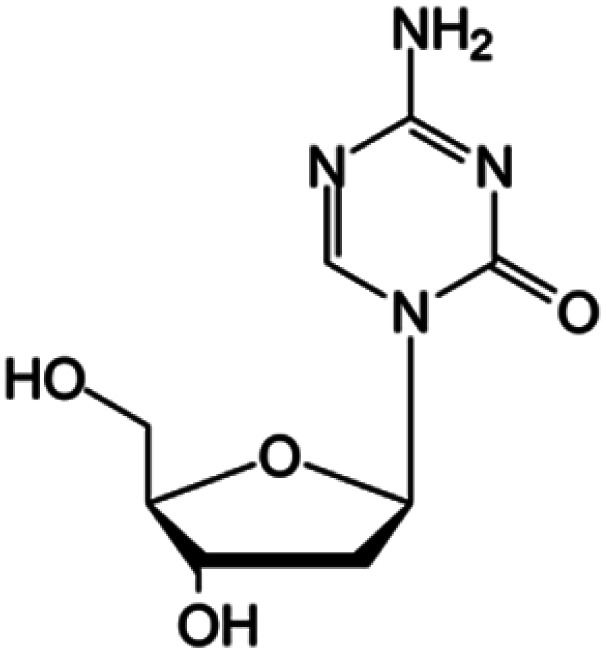
|
FDA approved (2006) | • Cytosine modification by azotation | • Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) | • DNA hypomethylation | 6 |
| EMA approved (2006) | • Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) | |||||
| Cladribine |
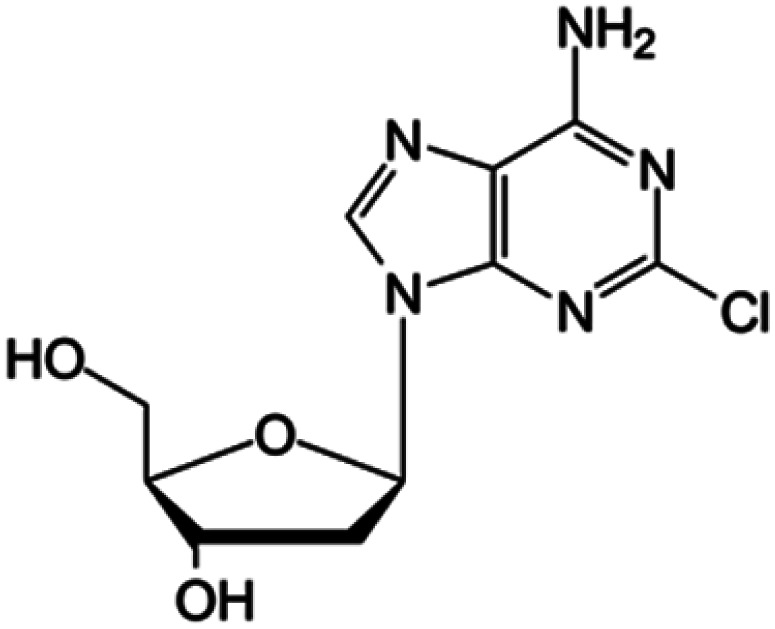
|
FDA approved (1993) | • Adenine modification by Cl-halogenation | • Hairy-cell leukemia | • Enzymatic depletion | 40 |
| EMA approved (2004) | • Non-Hodgkin lymphoma | • ATP accumulation | ||||
| Fludarabine |
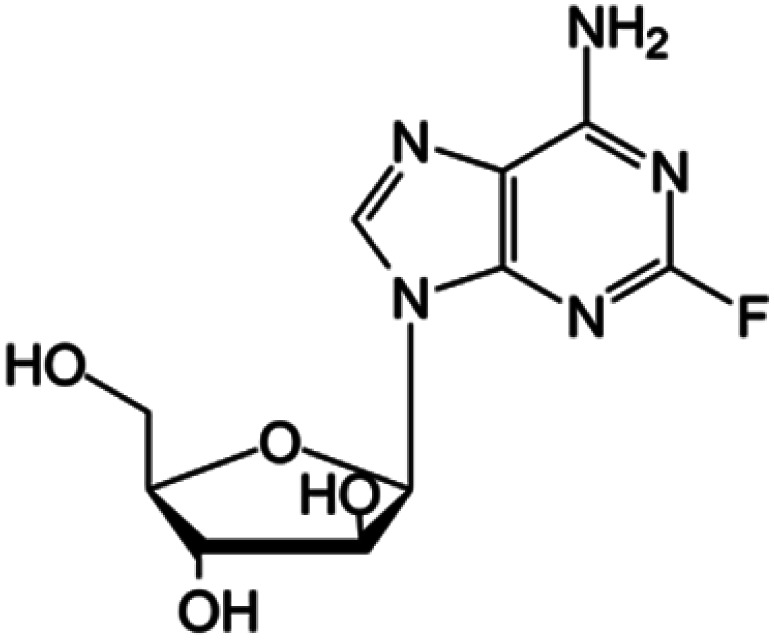
|
FDA approved (1991) | • Adenine modification by F-halogenation | • Chronic lymphocytic leukemia | • Nucleic acid synthesis inhibition | 41 |
| EMA approved (2014) | • Replacement of the ribose sugar ring with an arabinose | • Enzymatic inhibition | ||||
| Nelarabine |
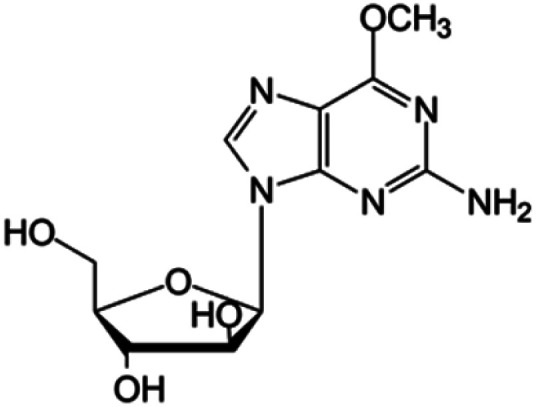
|
FDA approved (2005) | • Guanine by modification of a functional group | • T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia and lymphoma | • DNA synthesis inhibition | 42 |
| • Sugar ring is an arabinose instead of ribose |
Approval status was verified by the European Medicines Agency (http://www.ema.europa.eu) and the US Food and Drug Administration (http://www.fda.gov).
