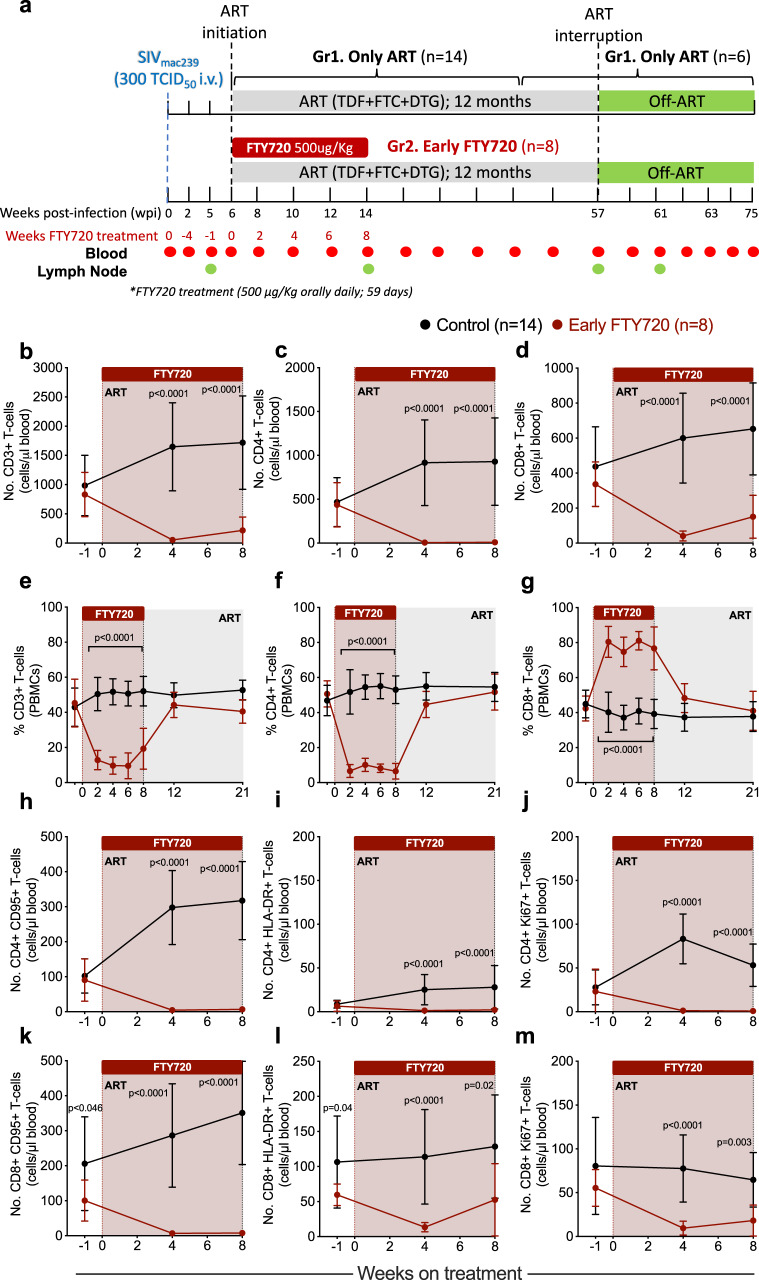
Fig. 1. FTY720 treatment in the first weeks of ART induces lymphopenia in SIV-infected RMs.
a Schematic of the study design. Twenty-two animals were infected with 300 TICD50 SIVmac239 and started antiretroviral treatment (ART) at week 6 post-infection (wpi). Animals were distributed into two groups: Gr1 received only ART (control group, n = 14 RMs), and Gr2 received 8 weeks of FTY720, starting at ART initiation (early FTY720, n = 8 RMs). Eight animals belonging to the control group were assigned to another study at ART interruption. b–d Absolute blood cell counts (cells/μl blood) and e–g frequencies of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) for b, e CD3+, c, f CD4+, and d, g CD8+ T cells from early FTY720 (n = 8 RMs) or control (n = 14 RMs) SIV-infected RMs. Absolute blood cell counts (cells/μl blood) for (h–j) CD4+ or (k–m) CD8+ T cells with a (h, k) memory (CD95+), i, l activated (HLA-DR+), and (j, m) cycling (Ki67+) phenotype in early FTY720 (red) or control (black) SIV-infected RMs. ART antiretroviral treatment. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. Statistical differences between FTY720 treated and control groups are indicated in asterisks and were assessed with a two-sided (95% CI) Mann–Whitney U-test.