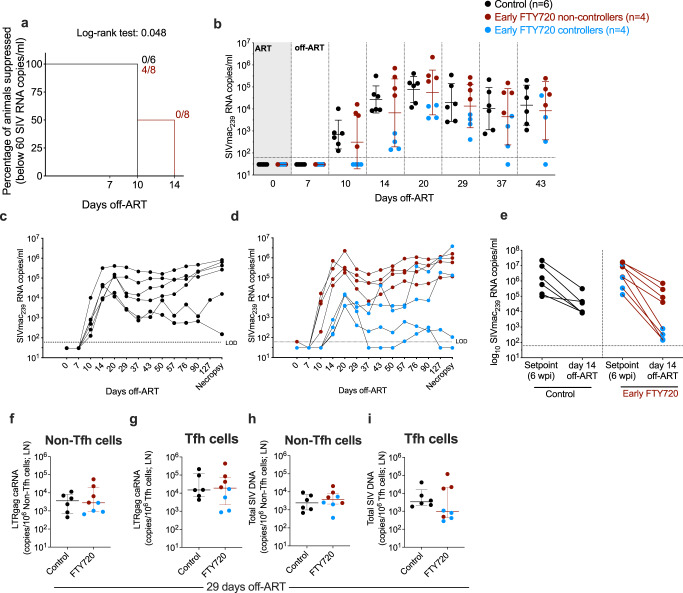
Fig. 4. A subset of FTY720 treated animals present reduced plasma viremia and Tfh infection in LN after ART interruption.
a Kaplan–Meier curve showing the percentage of animals maintaining plasma viral loads below 60 copies/ml in the first 2 weeks off-ART. b Plasma viral loads (SIVmac239 RNA copies/mL) measured by qRT-PCR longitudinally after ART interruption in early FTY720 non-controllers (n = 4 RMs), early FTY720 controllers (n = 4 RMs), or control (n = 6 RMs) SIV-infected RMs. Plasma viral loads (SIVmac239 RNA copies/mL) measured by qRT-PCR longitudinally in c control (n = 6 RMs), d early FTY720 non-controllers (n = 4 RMs), or early FTY720 controllers (n = 4 RMs) individual SIV-infected RMs after ART interruption. e Plasma viral loads (SIVmac239 RNA copies/mL) of early FTY720 non-controllers (n = 4 RMs), early FTY720 controllers (n = 4 RMs), or control (n = 6 RMs) SIV-infected RMs at setpoint (pre-ART, 6 wpi) and at day 14 off-ART. f, g Cell-associated SIV-RNA (LTRgag caRNA; copies/106 cells) and (h, i) cell-associated SIV-DNA (copies/106 cells) in f, h non-Tfh and g, i Tfh CD4+ memory T cells from LN of early FTY720 non-controllers (n = 4 RMs), early FTY720 controllers (n = 4 RMs), or control (n = 6 RMs) SIV-infected RMs at 29 days off-ART. ART antiretroviral treatment. Data in b are presented as the mean ± SD. Data in f–i are presented as the mean ± interquartile range. Statistical differences in a between FTY720 treated and control groups were assessed with a log-rank test.