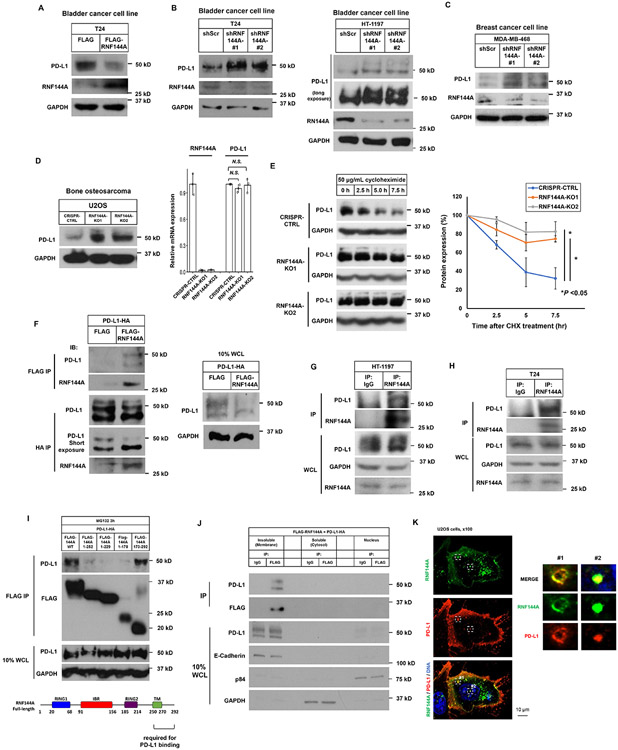
Figure 7. RNF144A interacts with PD-L1 in the plasma membrane and intracellular vesicles and decreases PD-L1 expression.
(A) Overexpression of RNF144A decreases the level of PD-L1 protein in T24 cells. T24 cells transiently transfected with a FLAG empty vector or FLAG-RNF144A expression vector were harvested, and the whole cell lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis to detect the indicated proteins.
(B-D) Knockdown or knockout of RNF144A increases the levels of PD-L1 in T24, HT-1197 (B) or MDA-MB-468 (C) cells stably expressing a scrambled shRNA or an RNF144A shRNA (#1 or #2) [13], or U2OS cells in which RNF144A was knocked out by an RNF144A sgRNA (KO1 or KO2) (D). Cells were harvested and the levels of PD-L1, RNF144A or GAPDH were detected by Western blot analysis. The mRNA levels of RNF144A and PD-L1 in U2OS cells were measured by qRT-PCR (right panel).
(E) Western blot analysis of endogenous PD-L1 to determine its half-life in RNF144A WT or KO cells. Cells were treated with 50 μg/ml cycloheximide (CHX) for the indicated time intervals, and the total cell lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis to determine the protein levels of PD-L1 or GAPDH. The intensity of PD-L1 or GAPDH was quantified using Image J software, and the relative level of PD-L1 was normalized to GAPDH (right panel).
(F) Co-immunoprecipitation experiment shows that transfected FLAG-RNF144A interacts with PD-L1-HA in Lenti-X 293T cells. The right panel shows 10% input of whole cell lysates (WCL) used in the co-immunoprecipitation.
(G-H) Endogenous RNF144A immunoprecipitates with endogenous PD-L1 in HT-1197 (G) or T24 (H) cells.
(I) Deletion analysis shows that the interaction of RNF144A with PD-L1 is mainly mediated by the carboxyl-terminal region (a.a. 250-292) of RNF144A. Truncated FLAG-RNF144A as indicated was transfected with PD-L1-HA in Lenti-X 293T cells. After 10 μM MG-132 treatment for 3 h to prevent protein degradation, co-immunoprecipitation was performed.
(J) Subcellular fractionation analysis shows that RNF144A interacts with PD-L1 mainly in the insoluble fraction, which contains the plasma membrane and intracellular vesicles. Lenti-X 293T cells were co-transfected with FLAG-RNF144A and PD-L1-HA. Cells were harvested in a hypotonic buffer on ice for 15 min, and subcellular fractionation was performed by differential centrifugation to enrich the nuclei, membrane-enriched insoluble fraction or cytosol as described in Materials and Methods.
(K) Immunofluorescence staining shows that RNF144A colocalizes with PD-L1 in the intracellular vesicles and plasma membrane. FLAG-RNF144A and PD-L1-HA were cotransfected to U2OS cells for 24 h. After fixation, immunostaining was performed using anti-FLAG mouse monoclonal antibody and Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated mouse secondary antibody to detect FALG-RNF144A. Subsequently, anti-HA rabbit antibody and Texas red-X-conjugated rabbit secondary antibody were used to stain PD-L1-HA. The nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33258. Right panels are magnified images of boxes #1 and #2.