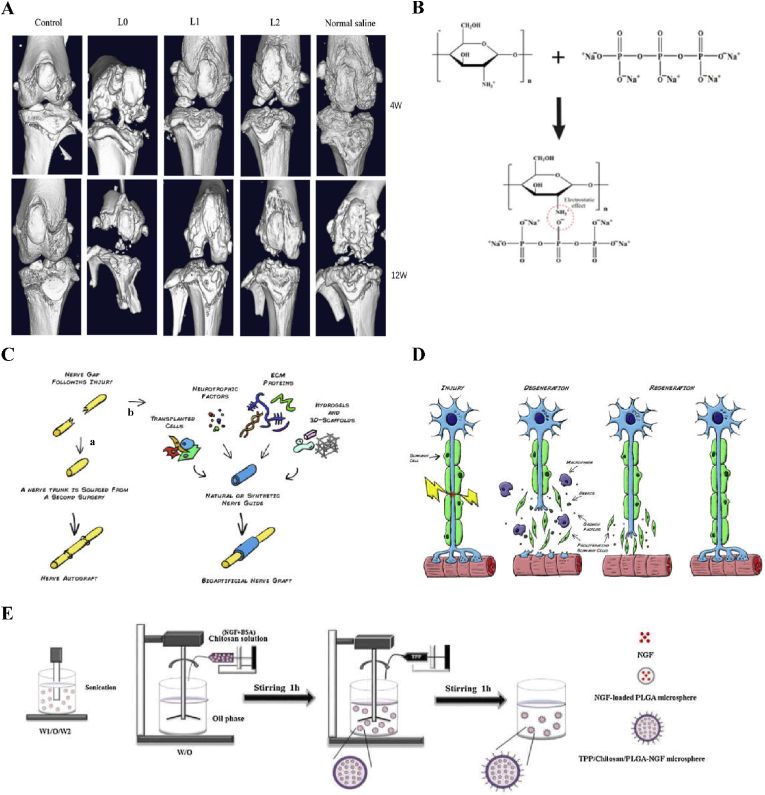
Fig. 7.
Effects of microspheres on bone, bioartificial nerve transplantation, molecular structure of crosslinked CS, Waller denaturation and preparation of microspheres by reemulsification and ion crosslinking. A Micro-CT scans showing the effect of microspheres on bone and articular cartilage injury. (Control group: Joint cavity was surgically accessed without any procedure done; L0: L0 microspheres injected after the ACLT and DMM procedures; L1, L1 microspheres injected after the ACLT and DMM procedures; L2, L2 microspheres injected after the ACLT and DMM procedures; Normal saline group: normal saline microspheres injected after the ACLT and DMM procedures). Reproduced with permission from Ref. [206]. Copyright 2021, Springer Nature. B Molecular structure of chitosan, TPP and TPP ionically cross-linked CS via electrostatic effect. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [88]. Copyright 2021, Elsevier. C Bioartificial nerve graft for nerve repair. As an alternative to autograft (a), the “gold standard” for nerve repair, the engineering of an artificial nerve graft (b) has been sought. Such graft will consist in a natural or synthetic nerve guide, which could be enriched with several factors to enhance axonal regrowth such as: 1) Transplantable cells, 2) neurotrophic factors or other pharmacological aids, 3) extra-cellular matrix (ECM) proteins and 4) hydrogels or 3D scaffolds as conduit fillers or cell/drug vehicles. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [208]. Copyright 2014, Elsevier. D Wallerian degeneration. Following injury, Schwann cells detach from the axons, start proliferating and help the recruited macrophages to clear the cellular and myelin debris. At the same time, expression of stimulating factors by SCs create a favourable environment for nerve regrowth towards the target organ. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [208]. Copyright 2014, Elsevier. E Schematic illustration of preparation of TPP/Chitosan/PLGA-NGF microspheres using a re-emulsification-ionic cross-linking method. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [88]. Copyright 2021, Elsevier. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)