Fig. 1.
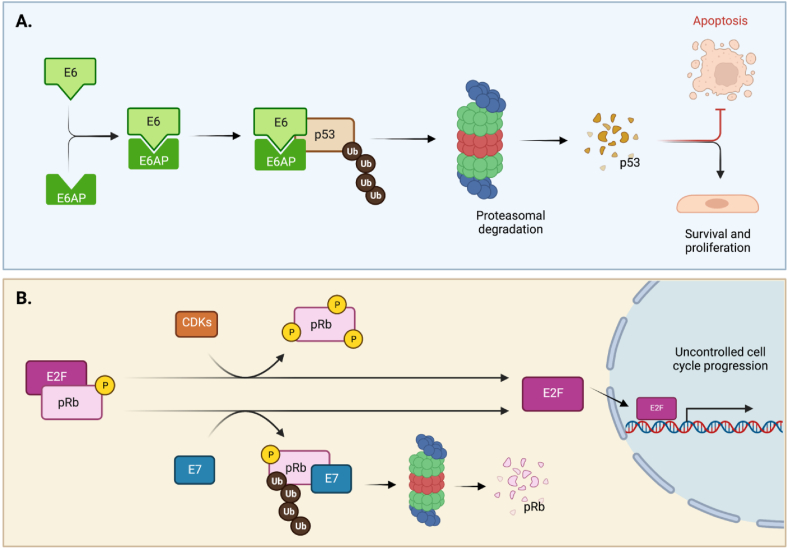
E6 and E7 HPV oncoproteins degrade p53 and pRb, respectively.
A. E6-induced p53 degradation through the formation of a ternary complex. Binding of E6 to p53 induces its ubiquitylation and proteasomal-mediated degradation, via the ubiquitin E3 ligase E6-associated protein (E6AP). B. Degradation of pRb, overexpression of CDKs and inactivation of CDK inhibitors all contribute to E2F overexpression and uncontrolled cell-cycle progression in cancers. Whereas hypo-phosphorylation of pRb prevents effects of E2F and renders cells quiescent, CDK/D-cyclin association causes its phosphorylation and release from E2F. Binding of E7 also causes release of E2F through ubiquitylation and proteasomal degradation of pRb [[163], [164], [165], [166], [167]].
Created withBioRender.com.