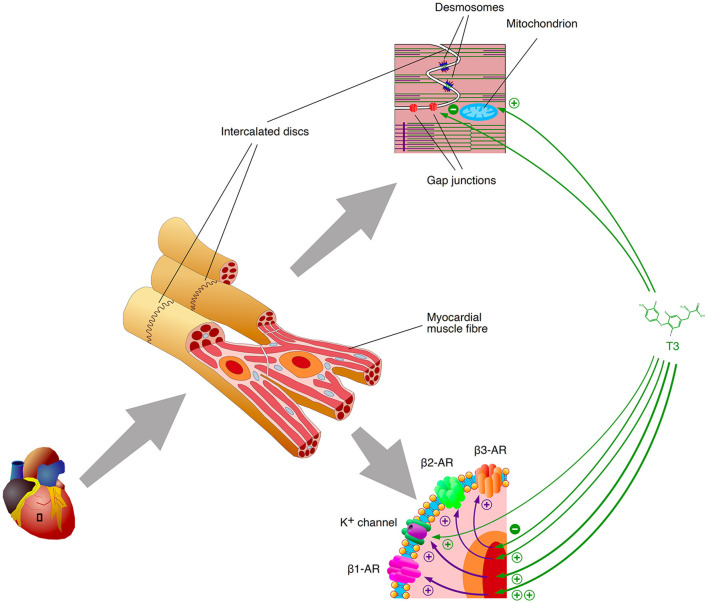
Figure 3.
Selected mechanisms of arrhythmogenesis by thyroid hormones. T3 (and other active thyroid hormones) upregulate the gene expression of beta1 and beta2 adrenoceptors via classical genomic signaling, but downregulate protective beta3 adrenoceptor expression. The transcription of critical genes for the formation of gap junctions is downregulated as well. Potassium channels are regulated via classical type 1 signaling and via non-genomic effects (type 4 action) as well. Purple arrows indicate the effects of gene expression (transcription, translation and associated processing steps), green arrows visualize the impact of T3-agonistic thyroid hormones.