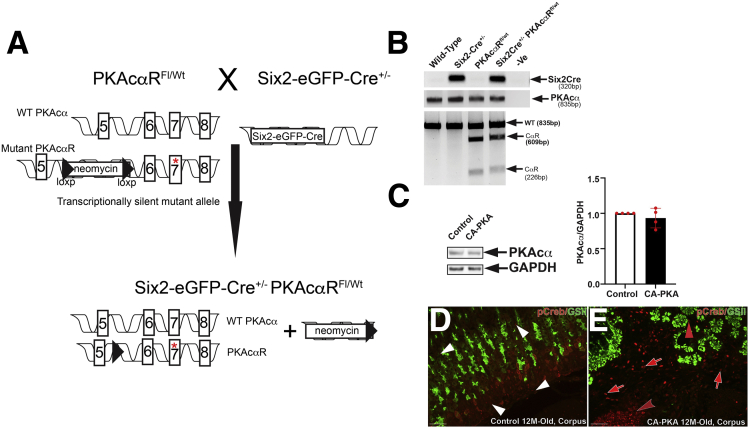
Figure 1.
Generation and characterization of CA-PKA mice.A, A schematic of the genetic construct and mating scheme of the CA-PKA mice.23B, The presence of the Cre transgene was detected by a polymerase chain reaction that generated a band of 320 bp. For detecting the floxed Prkaca allele, a 2-step genotyping protocol was used. First, an 835 bp segment of Prkaca was amplified from the tail DNA from all possible genotypes. In mice carrying the mutant floxed allele, the 835bp polymerase chain reaction product was partially digested and generated 609 bp and 226 bp fragments due to the presence of a unique restriction site for the enzyme Mlu. C, Representative immunoblot and quantification graph showing relative PKAcα levels in the mutant corpus vs control (n = 4). D, Images of corpus sections of 12-month-old control and CA-PKA mice co-stained with p-CREB (PKA activity) antiserum (red) and GSII-lectin (green, mucous neck cells). In control corpus, nuclear p-CREB signal was observed primarily in stromal cells (white arrowheads). In mutant corpus, stronger nuclear p-CREB signal was observed in mutant stromal cells vs control (red arrows), and the number of p-CREB+ stromal cells were also increased (red arrows). Infiltrated inflammatory cells that either formed tertiary follicles (red concave arrowhead) or scattered in the submucosa also were also strongly positive for p-CREB.; p-CREB signal was also observed in a subset of GSII+ cells in the mutant (red arrowhead). Scale bars = 50 μm.