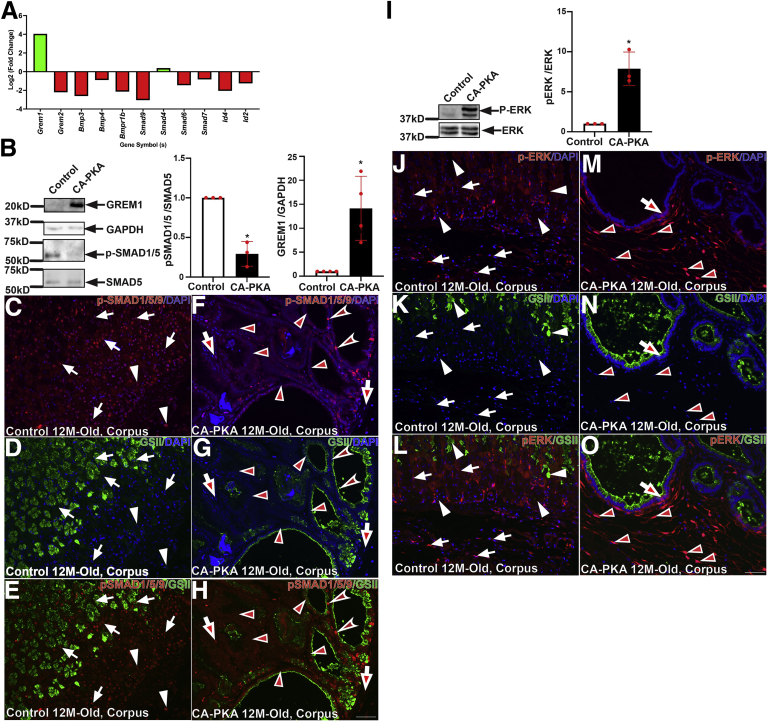
Figure 14.
BMP and ERK signaling is misregulated in CA-PKA corpus.A, Fold change (P < .05 or less) in BMP pathway components identified by RNAseq. B, Representative immunoblots and quantification graphs (∗P < .05) showing relative gremlin 1 (GREM1) and phospho-SMAD1/5 levels in the mutant corpus vs control. C–H, Corpus sections from 12-month-old control and CA-PKA mice co-stained with phospho-SMAD1/5/9 antiserum (red, BMP response) and GSII-lectin (green). In control corpus (C & E), phospho-SMAD1/5/9 signal was observed in epithelial (arrows) and stromal (arrowheads) compartments. In the mutant corpus (F & H), decreased phospho-SMAD1/5/9 signal is indicated in epithelial (arrowheads) and stromal (arrows) compartments; a few epithelial (concave arrowheads) with strong phospho-SMAD1/5/9 signal are indicated. I, Representative immunoblot and quantification graph (∗P < .05) showing phospho-ERK (n = 4) levels in the corpus of CA-PKA mutants vs control. J–O, Images of corpus sections of 12-month-old control and CA-PKA mice costained with p-ERK1/2 antiserum (red) and GSII-lectin (green). In control corpus (J–L), cytoplasmic p-ERK signal in parietal (white arrows) and stromal cells (white arrowheads) is indicated. In mutant corpus (M–O), nuclear p-ERK signal in stromal cells (arrowheads) and cytoplasmic p-ERK signal an epithelial cell (arrow) is shown. Scale bars = 50 μm. Blue (DAPI).