Figure 3.
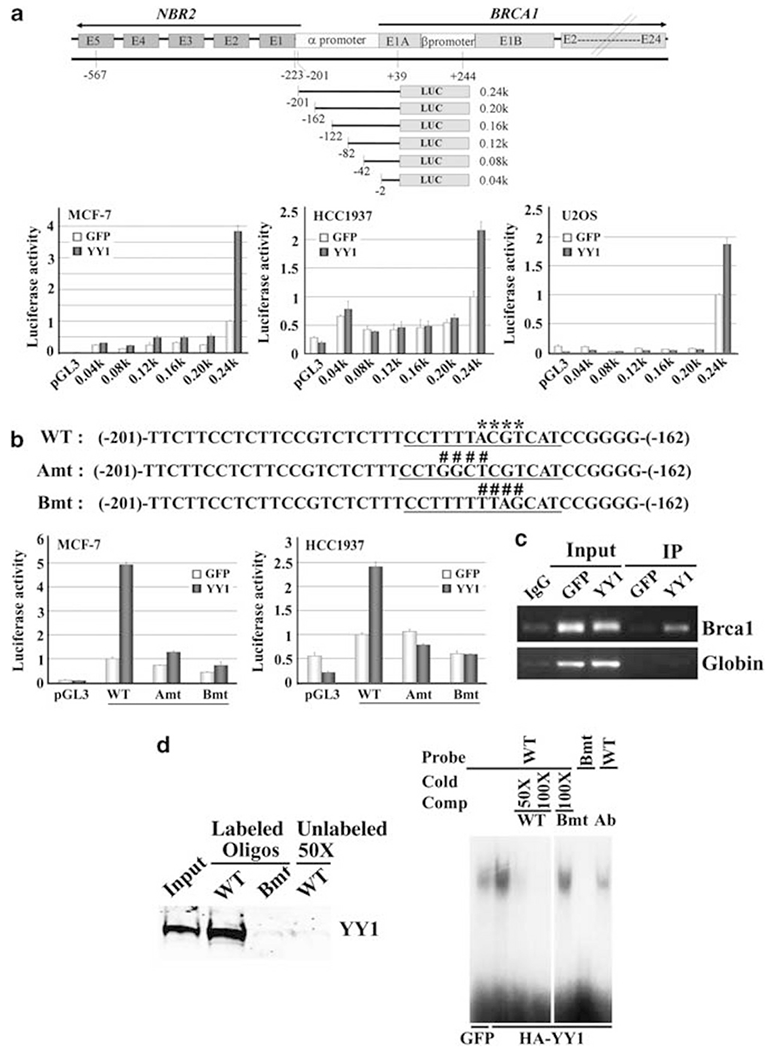
YY1 interacts with BRCA1 promoter and positively regulates its function. (a) Structures of BRCA1 and NRB promoter region and serial deletion from the 0.24-kb construct. Luciferase reporter assay of these constructs in MCF-7, HCC1937 and U2OS cells after co-transfection with constructs expressing either YY1 or GFP. (b) Wild-type (WT) and two mutant oligonucleotides (Amt and Bmt) within nucleotides −201 and −162. The putative Gli-Krueppel-related transcription factor YY1 binding site is underlined and the core sequence is marked with asterisks in the WT sequence. Both A and B mutations (Amt and Bmt, as marked with ####) diminished the induction of the BRCA1 promoter by YY1 in MCF-7 and HCC1937 cells. (c) ChIP assay to show YY1 binds to the BRCA1 promoter in MCF-7 cells transiently transfected with YY1. (d) Biotin-streptavidin pull-down assay (left side) and electrophoretic mobility shift assay (right side). Each reaction for biotin-streptavidin pull-down assay used 1 μg biotin-labeled oligonucleotide and 300 μg extract from HeLa cells transiently transfected with YY1. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay showing that the wild-type oligo, but not Bmt oligo, had reduced migration, which could be competed off in the presence of cold wild-type oligo, but not mutant oligo.
