Fig. 5 |. HIV-resistant Dual-CAR T cells mediate superior virus-specific immune responses.
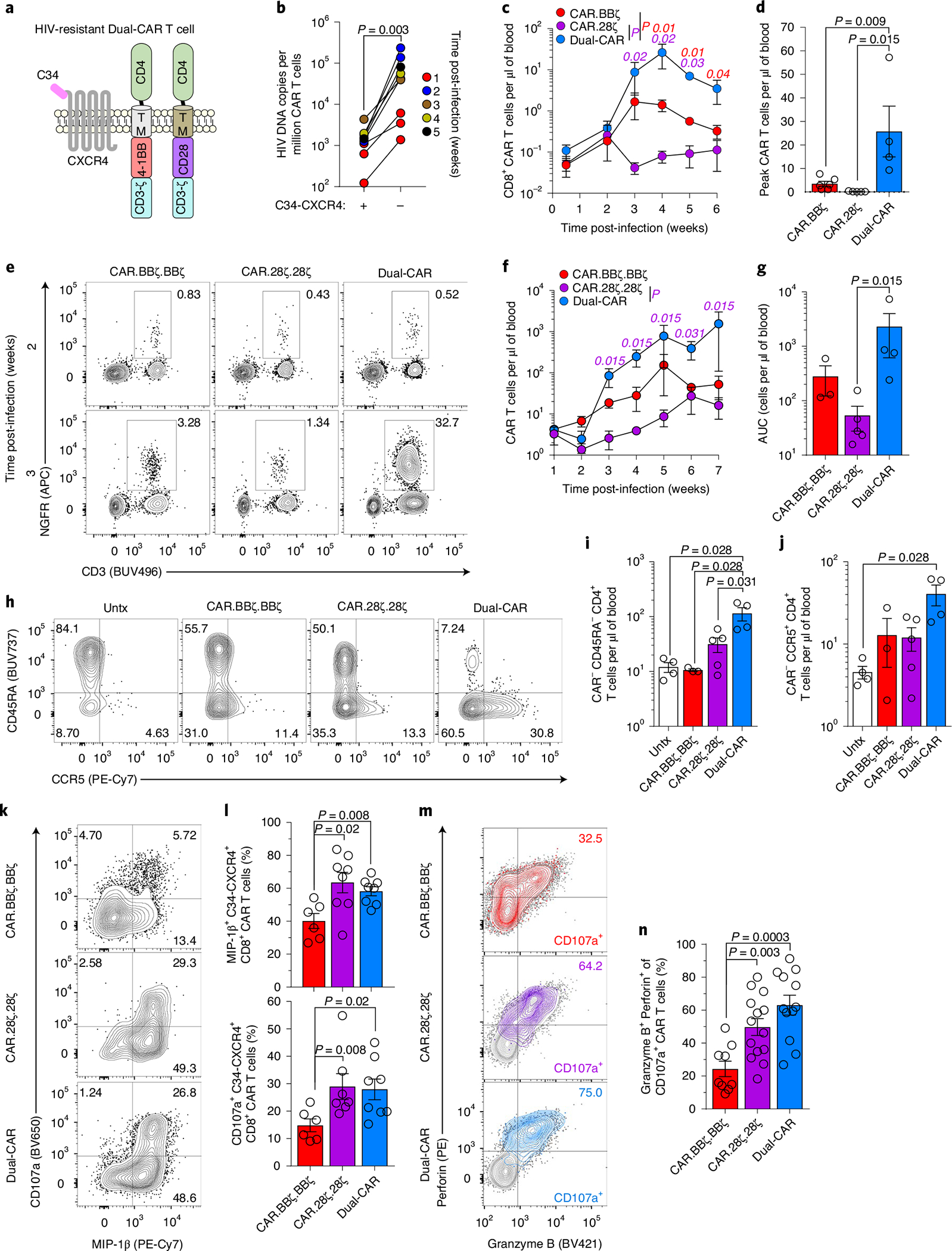
a, Schematic of HIV-resistant (C34-CXCR4+) Dual-CAR T cells. b, HIVJRCSF-infected BLT mice received 107 CAR T cells at 48 h postchallenge. HIV DNA load in sorted CAR T cells from individual mouse splenic tissue (n = 8). c,d, HIVMJ4-infected mice were infused at 48 h postchallenge with 106 C34-CXCR4+, CAR.BBζ (n = 6), CAR.28ζ (n = 5) or purified Dual-CAR (n = 4) T cells. Longitudinal peripheral concentration (c) and peak peripheral CAR T cell concentration (d). e–n, HIVMJ4-infected mice were infused at 48 h postchallenge with 106 C34-CXCR4+, purified CAR.BBζ.BBζ (n = 5), CAR.28ζ.28ζ (n = 5) or Dual-CAR (n = 5) T cells, or were untreated (n = 4). Purification strategy is described in Supplementary Fig. 10. e, Frequency of CAR T cell populations out of total human CD45+ cells 2 and 3 weeks post-infection. f,g, Longitudinal concentration (f) and cumulative peripheral CAR T cell persistence (g). h, FACS plots showing CCR5 expression within peripheral memory CD4+ T cells (CAR−). i,j, Concentration of total memory (i) and CCR5+ (j) CD4+ T cells (CAR−) at 6 weeks post-infection. k,l, FACS plots (k) and frequency (l) of MIP-1β+ and CD107a+ CD8+ CAR T cells from tissue at 8 weeks post-infection after ex vivo stimulation. m,n, Distribution (m) and frequency (n) of granzyme B+ perforin+ cells within CD107a+ CAR T cells from tissues after ex vivo stimulation. b, Two-sided Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test was used to calculate significance. For remaining analyses, significance was calculated using a two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum test. Bars and error bars indicate mean ± s.e.m., and symbols represent individual mice, except for c where symbols indicate mean. Sample sizes in these studies indicate biologically independent animals.
