Fig. 8. Epithelial HVEM is required for host defense against S. typhimurium infection.
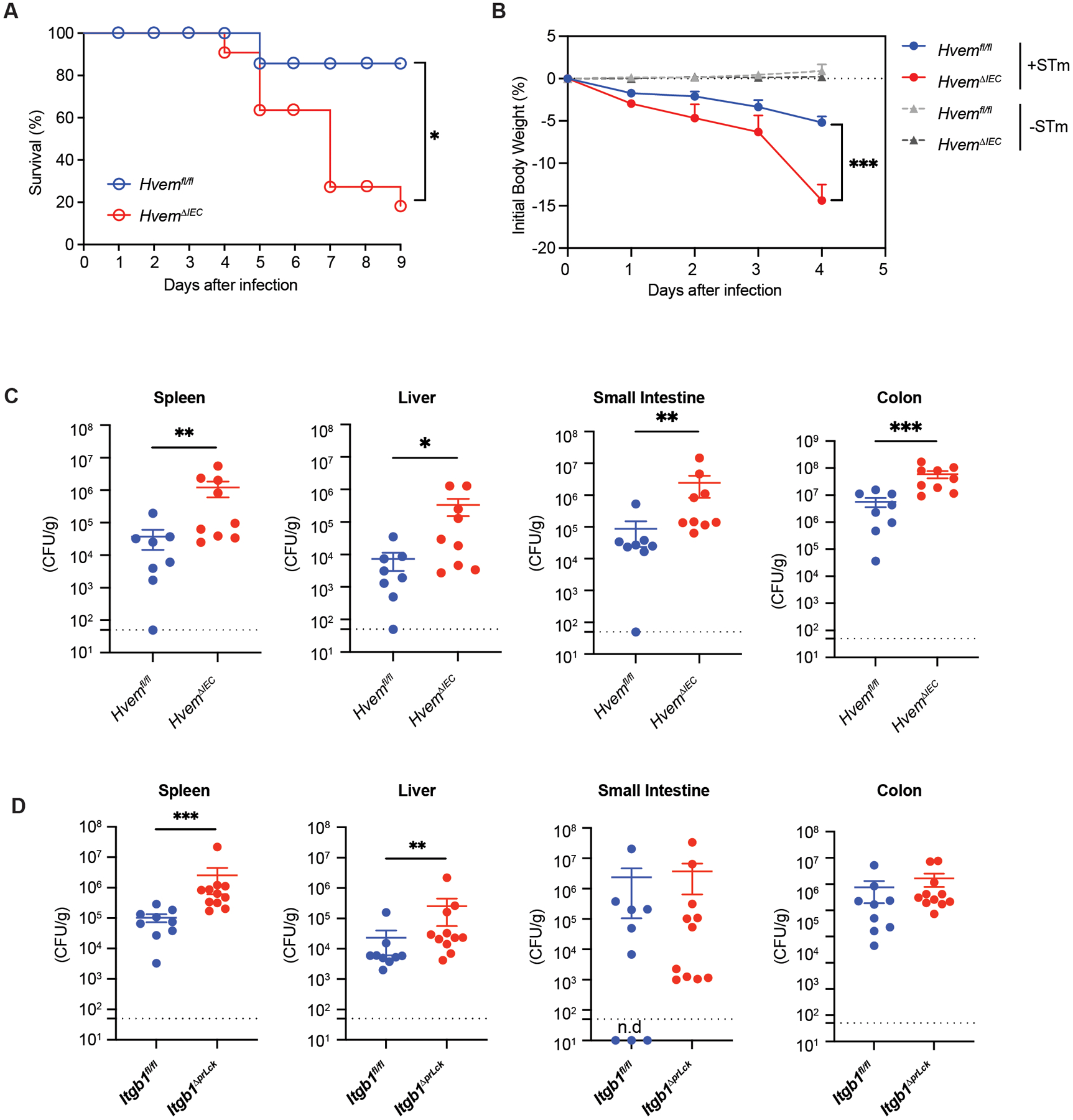
HvemΔIEC mice and control Hvemfl/fl mice were infected orally with 1 × 107 S. typhimurium colony-forming units (CFU)/mouse (A-C). (A) Survival curves (Hvemfl/fl, n=8; HvemΔIEC, n=11). (B) Changes in body weight (% change from baseline) (infected Hvemfl/fl, n=8; infected HvemΔIEC, n=9; uninfected Hvemfl/fl, n=11; uninfected HvemΔIEC, n=8). (C) Bacterial burdens at day 4 p.i. (Hvemfl/fl, n=8; HvemΔIEC, n=9). (D) Itgb1fl/fl (n=9) and Itgb1ΔprLck (n=11) mice were infected orally with S. typhimurium and bacterial burdens measured at days 3–4 p.i. Dashed line represents the limit of detection (C, D). Statistical analysis was performed using Log-rank test (A), 2 way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test (B), or Mann-Whitney test (C, D). Statistical significance is indicated by *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001. Data shown are means ± SEM (A). Bars show the mean, symbols represent individual mice. Data represent pooled results from at least two independent experiments having at least three mice per group in each experiment. Groups of co-housed littermates were analyzed.
