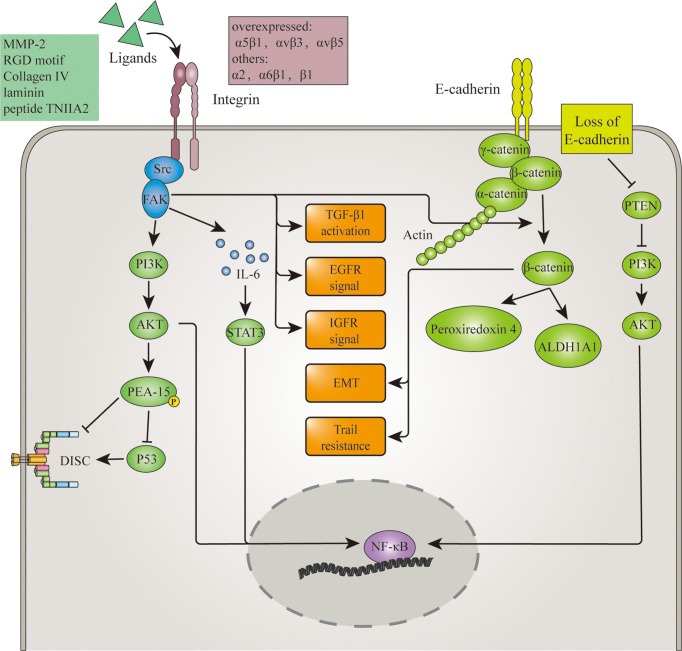
Figure 1.
Adhesion molecules involved in anoikis resistance mechanism of glioma. Overexpression of Integrins and loss of E-cadherin in glioma disrupt the initiating signal of anoikis. Upon cell detachment, overexpressed integrins still activate FAK, which in turn activates signalings such as TGFβ, EGFR, IGFR, PI3k/AKT pathway. Then through p53 inhibition, NF-κB activation or other mediators, these pathways lead to anoikis. α2 integrin induced FAK activation also promotes the release of β-catenin from the E-cadherin/β-catenin complex. Along with the loss of E-cadherin and the help of Wnt, this increased the cytoplasmic level of β-catenin. β-catenin thereby promote anoikis resistance through EMT, TRAIL resistance and upregulation of invasion-related protein ALDH1A1 and peroxiredoxin 4. Aside from β-catenin, loss of E-cadherin also downregulates tumor suppressor PTEN and therefore maintains NF-κB activation.