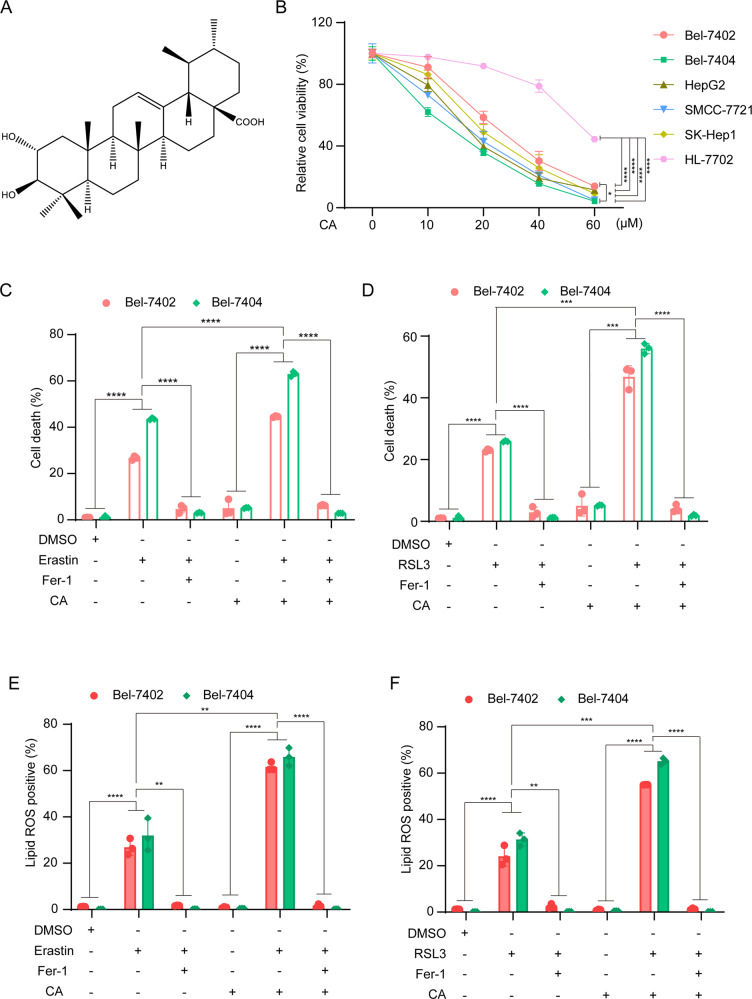
Fig. 1. CA increases the sensitivity of liver cancer cells to ferroptosis.
A Chemical structure of CA. B Established HCC cell lines (Bel-7402, Bel-7404, SMCC-7721, SK-Hep1, HepG2) and normal hepatocyte cell (HL-7702) were treated with a series of concentrations (0, 10, 20, 40, 60 μM) of CA for 24 h, and cell viability was determined by CCK-8 assay. C, D Bel-7402 and Bel-7404 cells were seeded at an appropriate density in six-well plates and cultured for 24 h, then treated with: 10 μM erastin or 5 μM RSL3; 10 μM CA; pretreatment with 10 μM CA for 1 h followed by 10 μM erastin or 5 μM RSL3; 2 μM ferroptosis inhibitor Fer-1, in complete medium for 24 h. Cell death was quantified by SYTOX-Green staining followed by flow cytometry. E, F Production of lipid ROS in (C, D) was measured by C11-BODIPY staining followed by flow cytometry after 10 h of drug treatment: 10 μM erastin or 5 μM RSL3; 10 μM CA; pretreatment with 10 μM CA for 1 h followed by 10 μM erastin or 5 μM RSL3. Data were analyzed using Student’s t test and expressed as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.