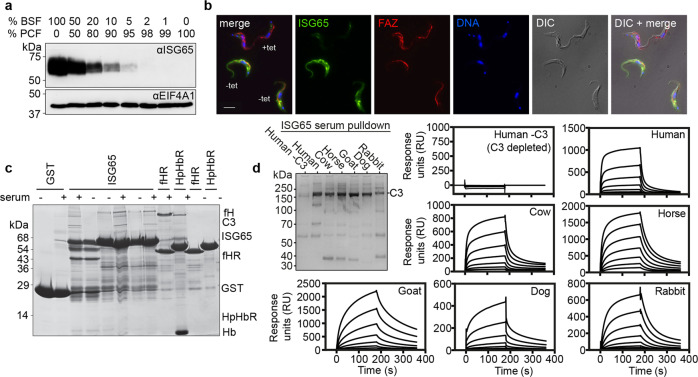
Fig. 1. Identification of ISG65 as a receptor for complement factor C3b.
a A Western blot showing extracts of bloodstream form (BSF) and procyclic form (PCF) trypanosomes, mixed in the proportions indicated above the blot. This blot (n = 1) was probed using polyclonal sera against ISG65 (αISG65) (upper panel) and by polyclonal sera against EIF4A1 (αEIF4A1) as a loading control (lower panel). b Immunofluorescence images showing ISG65 (green), flagellar marker, FAZ (red), and a DNA marker (blue). Trypanosome cells contain a tet-inducible RNAi knock-down construct for ISG65 and were either incubated with tet (tet+) or not (tet−) before mixing and imaging. The scale bar is 10 μm. Representative images are shown with n = 3. c An SDS-PAGE gel showing the outcome of pull-down experiments. Beads coated with GST and GST-fusions of ISG65A, the factor H receptor (fHR) and the haptoglobin-haemoglobin receptor (HpHbR) were incubated with bovine serum, before washing and elution. Bands eluted include factor H (fH), complement factor C3 (C3), and haemoglobin (Hb). n = 3. d Interaction of ISG65G with C3 from different species, showing broad specificity. The gel on the left shows a pull-down where ISG65 was attached to streptavidin beads then incubated with the serum of various mammals, n = 1. C3 is the predominant band in all cases except where human serum that was previously depleted of C3 (Human -C3) is used. Surface plasmon resonance traces are also shown for each serum, where ISG65 is immobilised via the C-terminus and binding of serum components from various species is determined.