TABLE 3.
Localization frequencies of and complementation by GFP-FtsL and GFP-FtsLEcol-MalF swap proteins
| Construct | Structurea | Localization frequencyb
|
Complementatione
|
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of cells scored | Band at midcell (%) | Swap not fused to GFPc | Swap fused to GFPd | ||
| GFP-FtsL |
 |
342 | 72 | +++ | +++ |
| GFP-LLL | 310 | 69 | +++ | +++ | |
| GFP-FLL | 307 | 70 | − | − | |
| GFP-FFL | 295 | <1 | − | ND | |
| GFP-LFL | 301 | <1 | − | ND | |
| GFP-LLF | 293 | <1 | ND | ND | |
| GFP-LLI | 320 | <1 | − | ND | |
| GFP-FFF | 311 | <1 | − | ND | |
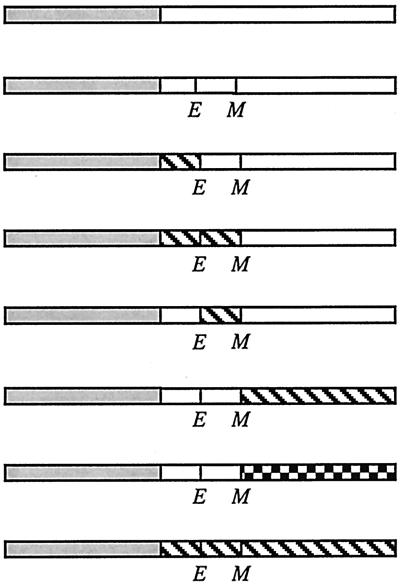
Open boxes represent domains of FtsL. Shaded boxes denote GFP. Hatched boxes represent domains derived from MalF. The checkered box represents the periplasmic domain of FtsI. E and M indicate borders of the transmembrane domain where restriction sites for EagI and MscI, respectively, have been introduced. In FtsL, the former changes a Lys to an Arg and the latter changes an Ala to Gly. Diagrams of fusion proteins are not to scale. The cytoplasmic and transmembrane domains of FtsL contain 37 and 20 amino acids, respectively, while those from MalF contain 16 and 25 amino acids, respectively. The periplasmic domain of FtsL contains 64 amino acids. The periplasmic domain of FtsI contains 537 amino acids. The region past the first transmembrane domain of MalF contains 478 amino acids.
Strains used: FtsL, EC438; LLL, JMG287; FLL, JMG469; FFL, JMG292; LFL, JMG289; LLF, JMG290; LLI, JMG295; FFF, JMG291.
Strains used: FtsL, strain from reference 10; LLL, JMG344; FLL, JMG348; FFL, JMG359; LFL, JMG347; LLI, strain from reference 10; FFF, strain from reference 10.
Strains used: GFP-FtsL, JMG366 (8); GFP-LLL, 367; GFP-FLL, JMG420.
For complementation test, plus signs indicate colony size and minus signs indicate no growth. ND, not determined.
