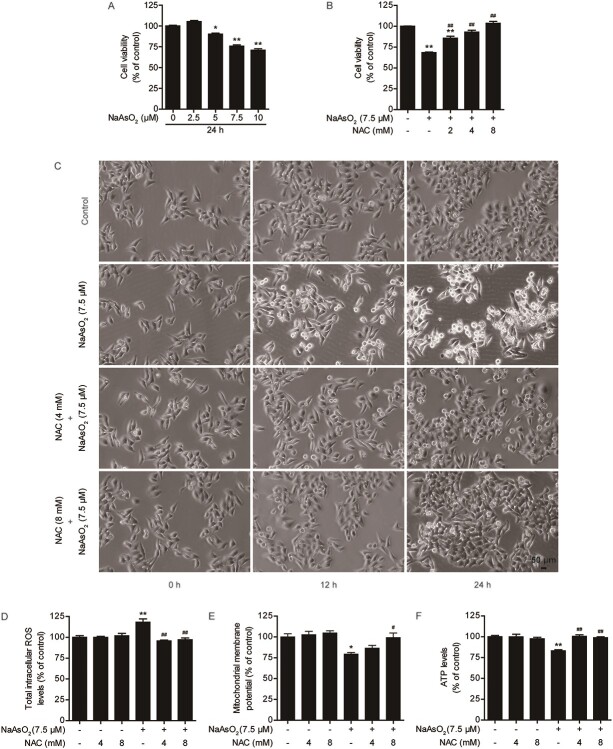
Fig. 1.
NAC relieves arsenic-induced cytotoxicity, intracellular ROS production and mitochondrial dysfunction in L02 cells. (A) Effects of different concentrations of arsenic on cell viability at 24 h after exposure. (B) Effects of NAC pretreatment for 4 h on the arsenic-induced decrease in cell viability at 24 h after exposure. (C) NAC pretreatment protects against arsenic-induced morphological damage, as observed under a light microscope at 10× magnification. (D) Changes in intracellular ROS levels at 3 h in the different treatment groups. (E) Changes in the mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) at 3 h in the different treatment groups. (F): Changes in intracellular ATP levels at 3 h in the different treatment groups. The data are presented as the mean ± SEM of four independent experiments. *P < .05, **P < .01 vs. the control group. #P < .05, ##P < .01 vs. the arsenic group.