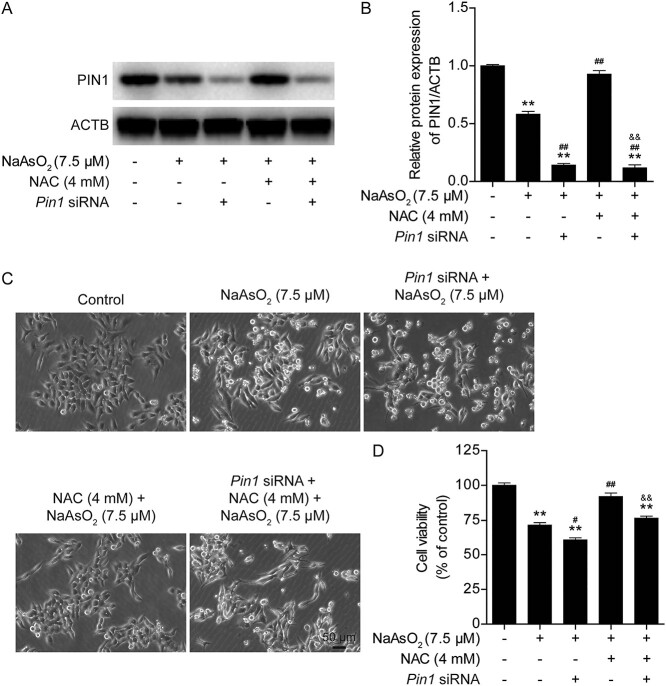
Fig. 5.
Knockdown of Pin1 abolishes the protective effects of NAC against arsenic-induced cytotoxicity in L02 cells. (A) Representative images of PIN1 protein expression after Pin1 siRNA transfection in the different treatment groups. (B) Semiquantification of PIN1 protein levels after Pin1 siRNA transfection in the different treatment groups. (C) Pin1 siRNA transfection exacerbated arsenic-induced morphological damage and disrupted the protective effect of NAC against arsenic-induced morphological damage, as observed under a light microscope at 10× magnification. (D) Pin1 siRNA transfection aggravated the arsenic-induced decline in cell viability and eliminated the protective effect of NAC against the arsenic-induced decline in cell viability. The data are presented as the mean ± SEM of four independent experiments. *P < .05, **P < .01 vs. the control group. #P < .05, ##P < .01 vs. the arsenic group. &P < .05, &&P < .01 vs. the NAC plus arsenic group.