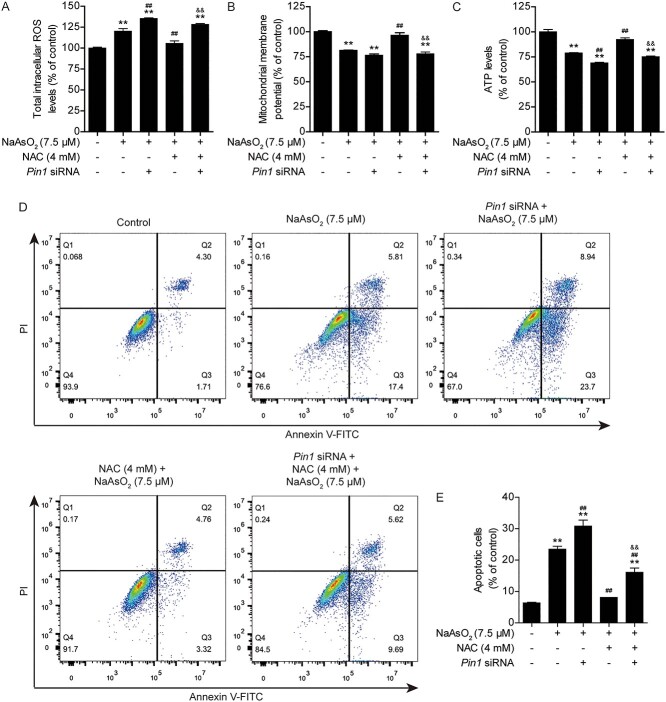
Fig. 6.
Knockdown of Pin1 abolishes the protective effects of NAC against arsenic-induced intracellular ROS production, mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis in L02 cells. (A) Changes in intracellular ROS levels in the different treatment groups. (B) Changes in the mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) in the different treatment groups. (C) Changes in intracellular ATP levels in the different treatment groups. (D) Pin1 siRNA transfection aggravated arsenic-induced apoptosis and abolished the protective effect of NAC against arsenic-induced apoptosis, as analyzed by flow cytometry. (F) Quantification of apoptotic cells in the different treatment groups. The data are presented as the mean ± SEM of four independent experiments. *P < .05, **P < .01 vs. the control group. #P < .05, ##P < .01 vs. the arsenic group. &P < .05, &&P < .01 vs. the NAC plus arsenic group.