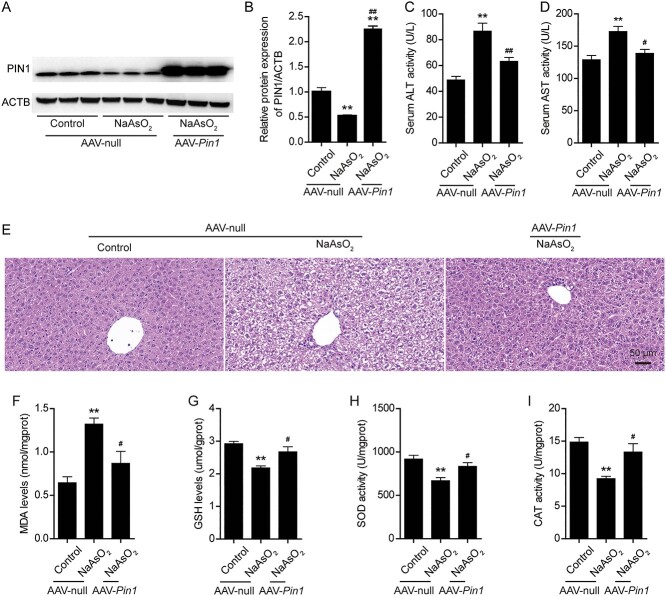
Fig. 7.
Pin1 overexpression mitigates arsenic-induced liver damage and oxidative stress in mice. (A) Representative images of PIN1 protein expression after AAV-Pin1 infection in mice from the different treatment groups. (B) Semiquantification of PIN1 protein levels after AAV-Pin1 infection in mice from the different treatment groups. (C) Changes in serum alanine transaminase (ALT) activity after AAV-Pin1 infection in mice from the different treatment groups. (D) Changes in serum aspartate transaminase (AST) activity after AAV-Pin1 infection in mice from the different treatment groups. (E) Representative images of hematoxylin and eosin showing liver damage after AAV-Pin1 infection in mice from the different treatment groups. Scale bar: 50 μm. (F-I) Changes in hepatic MDA levels (F), GSH levels (G), SOD activity (H) and CAT activity (I) after AAV-Pin1 infection in mice from the different treatment groups. The data are presented as the mean ± SEM of three or six mice. *P < .05, **P < .01 vs. the control group. #P < .05, ##P < .01 vs. the arsenic (AAV-null) group.