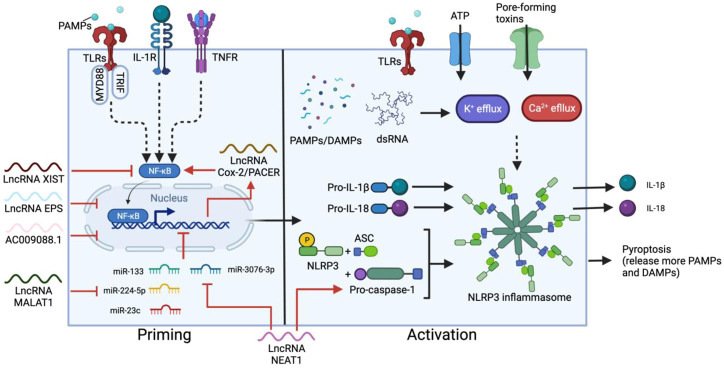
FIGURE 2.
Two-step activation of NLRP3 inflammasome and the main regulatory lncRNAs. The priming step can be triggered by ligand recognition of TLRs, cytokine (such as IL-1) receptors and TNF receptors (TNFR). NF-κB is then activated by myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MYD88) and TRIF in the TLR pathways, resulting in nuclear translocation of NF-κB and upregulation of NLRP3, pro-IL-18 and pro-IL-1β. A secondary signal, such as ATP, toxins, dsRNA, DAMPs and PAMPs stimulates the activation step, leading to the assembly of the inflammasome containing NLRP3, ASC and pro-caspace-1, which cleaves pro-IL-18 and pro-IL-1β into the mature cytokines. Most lncRNAs involved in this process regulate the priming step. XIST and PACER promotes or suppresses NF-κB activation respectively. In contrast, EPS, AC009088.1, MALAT1, and NEAT1 regulate the expression of primed genes. NEAT1 also participates in the activation step by stabilizing mature caspase-1 for inflammasome assembly.