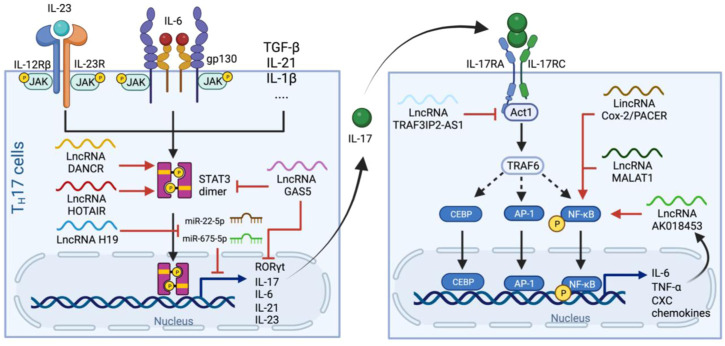
FIGURE 4.
Production and signaling pathways of IL-17 and regulatory lncRNAs in the process. Left panel. TH17 cells differentiate upon receiving IL-23, IL-6 and other cytokine signaling. Activated IL-6 and IL-23 receptors leads to phosphorylation and dimerization of STAT3 which subsequently initiates the expression of genes related to TH17 programming. LncRNAs such as DANCR and HOTAIR stimulate STAT3 dimerization in a similar manner to that of in the IL-6 pathway, whereas H19 sponges miR-22-5p and miR-675-5p to stimulate IL-17 production. GAS5 inhibits TH17 differentiation by promoting STAT3 degradation and suppresses RORγt and IL-17 expression. Right panel. IL-17 from TH17 cells dimerizes and binds to IL-17RA/C, which activates Act1 and then TRAF6 to facilitate nuclear translocation of CBEP, AP-1 and NF-κB and thus the release of IL-6, TNF-⍺ and CXCs. This pathway also induces the expression of the lncRNA AK018453, which, together with PACER and MALAT1, enhances NF-kB-mediated IL-17-dependent responses. Whereas TRAF3IP2-AS1 downregulated the expression of Act1 and suppress the effect of IL-17.